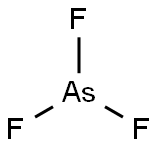
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Liquid; Fumes in air; [Merck Index] |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | OILY LIQUID |
| Boiling Point | 57.8 °C |
| Melting Point | -5.9 °C |
| Solubility | Soluble in ammonium hydroxide |
| Density | 2.7 |
| Vapor Pressure | 100 mm Hg @ 13.2 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | FUMES IN AIR |
| Decomposition | WHEN HEATED TO DECOMPOSITION IT EMITS HIGHLY TOXIC FUMES OF /ARSENIC & HYDROGEN FLUORIDE/. |
| Corrosivity | Etches glass |
| Other Experimental Properties | Decomposes in water |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Arsenic Compounds, Inorganic |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 131.91680 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 131.916804 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 131.916804 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Arsenic trifluoride is a fluoride of arsenic. Arsenic is a chemical element that has the symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a poisonous metalloid that has many allotropic forms: yellow (molecular non-metallic) and several black and grey forms (metalloids) are a few that are seen. Three metalloidal forms of arsenic with different crystal structures are found free in nature (the minerals arsenopyrite and the much rarer arsenolamprite and pararsenolamprite), but it is more commonly found as a compound with other elements. (T3)