75-15-0
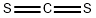
Product Name:
Carbon disulfide
Formula:
CS2
Synonyms:
Carbon Bisulfide;Carbon Disulfide
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Carbon disulfide appears as a clear colorless to light yellow volatile liquid with a strong disagreeable odor. Flammable over a wide vapor/air concentration range (1%-50%). Vapors are readily ignited; the heat of a common light bulb may suffice. Insoluble in water and more dense than water. Hence sinks in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used in the manufacture of rayon and cellophane, in the manufacture of flotation agents and as a solvent. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Mobile ... liquid |
| Odor | Purest distillates have sweet, pleasing, and ethereal odor ... usual commercial and reagent grades are foul smelling |
| Boiling Point | 116 °F at 760 mmHg (EPA, 1998) |
| Melting Point | -167 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Flash Point | -22 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | less than 1 mg/mL at 68 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Density | 1.2632 at 68 °F (EPA, 1998) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Density | 2.67 (EPA, 1998) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 360 mmHg at 77 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| LogP | log Kow = 1.94 |
| Henry's Law Constant | Henry's Law constant = 1.44X10-2 atm-cu m/mole at 24 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable under recommended storage conditions. |
| Autoignition Temperature | 194 °F (ICSC, 2023) |
| Decomposition | Decomposes on standing for a long time. |
| Viscosity | Coefficient of viscosity = 0.363 at 20 °C |
| Corrosivity | Carbon disulfide is normally stored and handled in mild steel equipment. ... Copper and copper alloys are attacked by carbon disulfide and must be avoided. |
| Heat of Combustion | -5814 btu/lb = -3230 cal/g = -135.2X10+5 J/kg |
| Heat of Vaporization | 84.1 cal/g at BP |
| Surface Tension | 32.25 dynes/cm at 20 °C |
| Ionization Potential | 10.08 eV |
| Odor Threshold | Odor Threshold Low: 0.01 [mmHg] Odor Threshold High: 0.42 [mmHg] Odor threshold from AIHA |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction = 1.6319 at 20 °C |
| Relative Evaporation Rate | 22.6 (Butyl acetate = 1) |
| Kovats Retention Index | 512 539 517 515 530 533.5 537 537 537 530 517.5 523.7 527 518 524 513 514 524 527 517 512 524 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Dipole moment 0.0; heat of fusion 1.049 kcal/mole; heat capacity at 24.3 °C: 18.17 cal/mole/deg; ebullioscopic constant 2.35 deg; dielectric constant 2.641 at low frequencies. Burns with blue flame to carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide; azeotrope with water bp 42.6 °C, contains 97.2% carbon disulfide |
| Chemical Classes | Solvents -> Other Solvents |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 76.15 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 75.94414235 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 75.94414235 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 64.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 3 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 18.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | No |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Pure carbon disulfide is a colorless liquid with a pleasant odor that is like the smell of chloroform. The impure carbon disulfide that is usually used in most industrial processes is a yellowish liquid with an unpleasant odor, like that of rotting radishes. Carbon disulfide evaporates at room temperature, and the vapor is more than twice as heavy as air. It easily explodes in air and also catches fire very easily. In nature, small amounts of carbon disulfide are found in gases released to the earth’s surface as, for example, in volcanic eruptions or over marshes. Commercial carbon disulfide is made by combining carbon and sulfur at very high temperatures
