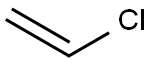
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Vinyl chloride appears as a colorless gas with a sweet odor. Easily ignited. Shipped as a liquefied gas under own vapor pressure. Contact with the unconfined liquid may cause frostbite by evaporative cooling. Leaks may be liquid or vapor. Vapors are heavier than air. May asphyxiate by the displacement of air. Under prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat the containers may rupture violently and rocket. Suspected carcinogen. Used to make plastics, adhesives, and other chemicals. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Colorless gas or liquid (below 77 degrees F) [Note: Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas] |
| Odor | Ethereal odor |
| Boiling Point | 7 °F at 760 mmHg (NTP, 1992) |
| Melting Point | -245 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Flash Point | -110 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble (NTP, 1992) |
| Density | 0.969 at 8.6 °F (USCG, 1999) - Less dense than water; will float |
| Vapor Density | 2.21 (NIOSH, 2023) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 3877.5 mmHg (USCG, 1999) |
| LogP | log Kow = 1.46 |
| Henry's Law Constant | Henry's Law constant = 0.0278 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | An unstable polyperoxide is apparently formed in vinyl chloride through oxidation by atmospheric oxygen in the presence of any of a variety of contaminants. Storage under these conditions for a long period increases the concentration of unstable polyperoxide to hazardous levels. |
| Autoignition Temperature | 882 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition is emits highly toxic fumes of /chloride/. |
| Viscosity | 0.01072 cP at 101.325 kPa, 20 °C (gas); 0.280 cP at -20 °C (liquid) |
| Corrosivity | Vinyl chloride is not corrosive when dry but in presence of moisture it corrodes iron and steel. |
| Heat of Vaporization | 160 Btu/Lb = 88 cal/g = -189.1X10+5 J/kg |
| Surface Tension | 23.1 dyn/cm at -20 °C |
| Ionization Potential | 9.99 eV |
| Polymerization | Polymerization occurs if heated in sunlight or presence of air; reaction is exothermic. |
| Odor Threshold | Odor Threshold Low: 10.0 [ppm] Odor Threshold High: 20.0 [ppm] Odor threshold from AIHA |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.3700 at 20 °C/D |
| Kovats Retention Index | 386 366 378 358.5 353 372.3 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Liquifies in freezing mixture |
| Chemical Classes | Plastics & Rubber -> Vinyl Halides |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H220:Flammable gases H225:Flammable liquids H280:Gases under pressure H350:Carcinogenicity H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P410+P403:Protect from sunlight. Store in a well-ventilated place. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 62.50 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 61.9923278 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 61.9923278 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 3 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 10.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Vinyl chloride is a colorless gas. It burns easily and it is not stable at high temperatures. It has a mild, sweet odor. It is a manufactured substance that does not occur naturally. It can be formed when other substances such as trichloroethane, trichloroethylene, and tetrachloroethylene are broken down. Vinyl chloride is used to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC is used to make a variety of plastic products, including pipes, wire and cable coatings, and packaging materials. Vinyl chloride is also known as chloroethene, chloroethylene, and ethylene monochloride.