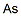CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Arsenic appears as a grayish metallic solid that turns black upon exposure to air. Insoluble in water. Toxic by ingestion. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | IT EXISTS IN THREE ALLOTROPIC FORMS, THE YELLOW (ALPHA), BLACK (BETA) AND GREY (GAMMA) FORMS |
| Odor | ... Odorless ... |
| Taste | NEARLY TASTELESS |
| Boiling Point | 1135 °F at 760 mmHg (sublimes) (USCG, 1999) |
| Melting Point | 1135 °F (Sublimes) (NIOSH, 2023) |
| Solubility | Insoluble (NIOSH, 2023) |
| Density | 5.727 at 77 °F (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Pressure | 0 mmHg (approx) (NIOSH, 2023) |
| Stability/Shelf Life | LOSES ITS LUSTER ON EXPOSURE TO AIR, FORMING A BLACK MODIFICATION + AS2O3 |
| Autoignition Temperature | 180 °C |
| Decomposition | When arsenic is heated in air it will burn and form a white smoke consisting of arsenic trioxide (As2O3). |
| Heat of Vaporization | 11.2 kcal/g-atom |
| Other Experimental Properties | A yellow modification which has no metallic properties is obtained by sudden cooling of arsenic-vapor. This yellow arsenic is converted back to the gray modification upon very short exposure to ultraviolet light. |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Arsenic Compounds, Inorganic |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H350:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 74.92159 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 74.921595 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 74.921595 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 1 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 0 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Arsenic is a naturally occurring element widely distributed in the earth's crust. In the environment, arsenic is combined with oxygen, chlorine, and sulfur to form inorganic arsenic compounds. Arsenic in animals and plants combines with carbon and hydrogen to form organic arsenic compounds. Inorganic arsenic compounds are mainly used to preserve wood. Copper chromated arsenic (CCA) is used to make "pressure-treated" lumber. CCA is no longer used in the U.S. for residential uses; it is still used in industrial applications. Organic arsenic compounds are used as pesticides, primarily on cotton plants.