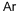CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Argon appears as a colorless odorless noncombustible gas. Heavier than air and can asphyxiate by displacement of air. Exposure of the container to prolonged heat or fire can cause it to rupture violently and rocket. If liquefied, contact of the very cold liquid with water may cause violent boiling. If the water is hot, there is the possibility that a liquid "superheat" explosion may occur. Contacts with water in a closed container may cause dangerous pressure to build. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Colorless monatomic gas |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Boiling Point | -185.847 °C |
| Melting Point | -186.36 °C triple point (69 kPa) |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic liquids |
| Density | 1.633 g/L |
| Vapor Density | 1.38 (Air = 1) |
| LogP | 0.74 |
| Heat of Vaporization | Liquid (normal BP): 6469 J/mol; Solid: (triple pt): 7.785 kJ/mol. |
| Other Experimental Properties | A noble gas characterized by an electronic structure in which the outer p subshell is entirely filled |
| Chemical Classes | Toxic Gases & Vapors -> Simple Asphyxiants |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Warning |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Gas Cylinder Compressed Gases GHS04 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H280:Gases under pressure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P410+P403:Protect from sunlight. Store in a well-ventilated place. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 39.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 39.96238312 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 39.96238312 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 1 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 0 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Argon appears as a colorless odorless noncombustible gas. Heavier than air and can asphyxiate by displacement of air. Exposure of the container to prolonged heat or fire can cause it to rupture violently and rocket. If liquefied, contact of the very cold liquid with water may cause violent boiling. If the water is hot, there is the possibility that a liquid "superheat" explosion may occur. Contacts with water in a closed container may cause dangerous pressure to build.