CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 165 °C |
| Solubility | 500000 mg/L |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.00000162 [mmHg] |
| LogP | 0 |
| Ionization Efficiency | Positive |
| Collision Cross Section | 130.5 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)] |
| Chemical Classes | Biological Agents -> Vitamins and Derivatives |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 167.16 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 167.058243149 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 167.058243149 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 70.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 162 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
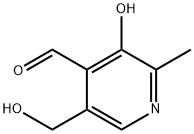
Pyridoxal is a pyridinecarbaldehyde that is pyridine-4-carbaldehyde bearing methyl, hydroxy and hydroxymethyl substituents at positions 2, 3 and 5 respectively. The 4-carboxyaldehyde form of vitamin B6, it is converted into pyridoxal phosphate, a coenzyme for the synthesis of amino acids, neurotransmitters, sphingolipids and aminolevulinic acid. It has a role as a cofactor, a human metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a vitamin B6, a pyridinecarbaldehyde, a member of methylpyridines, a monohydroxypyridine and a hydroxymethylpyridine. It is a conjugate base of a pyridoxal(1+).