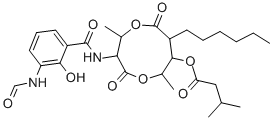
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Antimycin a is a solid. Specific uses for Antimycin A were not found. Antimycin A1,and Antimycin A3 are reported as antibiotics produced by Streptomyces for use as a fungicide and possibly as an insecticide and miticide. Registered only as a pesticide in the U.S. (EPA, 1998) |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Crystals |
| Melting Point | 300.2 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, chloroform; slightly soluble in benzene, carbon tetrachloride, petroleum ether. Insoluble in water. |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/. |
| Chemical Classes | Biological Agents -> Bacterial Toxins |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 548.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 5.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 548.27338086 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 548.27338086 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 157 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 849 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Antimycin a is a solid. Specific uses for Antimycin A were not found. Antimycin A1,and Antimycin A3 are reported as antibiotics produced by Streptomyces for use as a fungicide and possibly as an insecticide and miticide. Registered only as a pesticide in the U.S. (EPA, 1998)