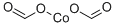CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Cobaltous formate is a red crystalline solid. It is soluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit the spread to the environment. It is used to make catalysts for use in chemical manufacture. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Red crystalline solid |
| Boiling Point | Becomes anhydrous at 284.0 °F Decomposes at 175 °C. (USCG, 1999) |
| Solubility | Solubility: 5.030 lb/100 lb at 68 °F /Cobalt(II) formate dihydrate/ |
| Density | 2.13 at 71.6 °F dihydrate (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Decomposition | Decomposes at 175 °C. |
| pH | Salts, basic, such as cobaltous formate, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. |
| Other Experimental Properties | Red crystalline powder; soluble in water, almost insoluble in alcohol; becomes anhydrous at 140 °C /Cobalt(II) formate dihydrate/ |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Metals, Inorganic Compounds |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 148.97 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 148.928502 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 148.928502 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 80.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 7.5 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Cobaltous formate is a red crystalline solid. It is soluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit the spread to the environment. It is used to make catalysts for use in chemical manufacture.