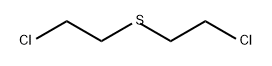
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Mustard gas is a clear amber colored oily liquid with a faint odor of mustard/garlic. It is not readily combustible. Its vapors are heavier than air, are very toxic, and can be absorbed through the skin. The effects from exposure to the material include blindness which may be delayed. Prolonged exposure of the container to fire or intense heat may cause it to violently rupture and rocket. Mustard gas is also known as dichlorodiethyl sulfide. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Colorless, oily liquid when pure |
| Odor | Weak, sweet, agreeable odor |
| Boiling Point | 419 to 423 °F at 760 mmHg (EPA, 1998) |
| Melting Point | 55 to 57 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Flash Point | 221 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | In water, 609 mg/L at 25 °C |
| Density | 1.274 at 68 °F (EPA, 1998) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Density | 5.4 (EPA, 1998) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.09 mmHg at 86 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| LogP | log Kow = 2.14 /Estimated by EVA (Experimental Value Adjusted) method using measured value of bis(2-chloroethyl) ether (1.29)/ |
| Henry's Law Constant | Henry's Law constant= 2.45X10-5 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | HYDROLYZED IN AQ SOLN (HALF-LIFE: 5 MIN AT 37 °C) |
| Decomposition | In pure aqueous media, most sulfur mustard is hydrolyzed to thiodiglycol and hydrochloric acid. |
| Viscosity | 3.95 cS at 20 °C |
| Corrosivity | Rapidly corrosive to brass at 65 °C; will corrode steel at a rate of .0001 in. of steel per month at 65 °C |
| Odor Threshold | 1.30X10-3 mg/L (gas) (detection in air, chemically pure) |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.5313 at 20 °C |
| Kovats Retention Index | 1136 1124 1123.8 1124.8 1175 1131 1124 1124 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Reacts with sulfhydryl and imidazole groups; products of hydrolysis are thiodiglycol and hydrochloric acid |
| Chemical Classes | Toxic Gases & Vapors -> Chemical Weapons |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 159.08 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 157.9723768 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 157.9723768 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 25.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 28.9 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Sulfur mustard (HD) is a thick liquid at ambient temperature, but becomes a solid at 58 °F. It is heavier than water as a liquid and heavier than air as a vapor. It does not occur naturally in the environment It is often called mustard gas, but sulfur mustard is not likely to change into a gas immediately if it is released at ordinary temperatures. As a pure liquid, it is colorless and odorless, but when mixed with other chemicals, it looks brown and has a garlic-like smell. Sulfur mustard has been used in chemical warfare and was made in large amounts during World Wars I and II. It was reportedly used in the Iran-Iraq war in 1980-1988. It is not presently used in the United States, except for research purposes, and the U.S. Department of Defense must destroy all remaining stocks of sulfur mustard by 2004.