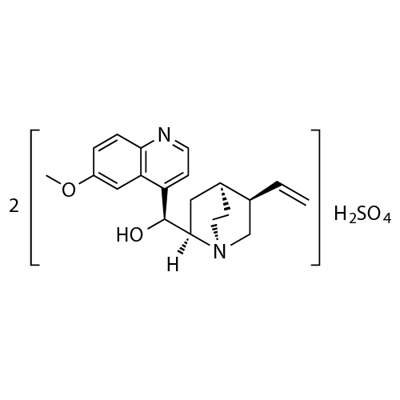
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Color/Form | Occurs as fine, needle-like, white crystals which frequently cohere in masses or as a fine, white powder. |
|---|---|
| Taste | Very bitter taste |
| Solubility | WHITE; VERY BITTER; ODORLESS; FINE CRYSTALS; FREQUENTLY COHERING IN MASSES; PH (1% AQUEOUS SOLN): 6.0-6.8 PKA: 4.2, 8.8; SPECIFIC OPTICAL ROTATION: +212 @ 25 °C/D (95% ALCOHOL); ABOUT + 260 @ 25 °C/D (DILUTE HYDROCHLORIC ACID); DOES NOT LOSE ALL OF ITS WATER BELOW 120 °C 1 G DISSOLVES IN ABOUT 90 ML WATER, 15 ML BOILING WATER, 10 ML ALCOHOL, 3 ML METHANOL, 12 ML CHLOROFORM; INSOL IN ETHER, BENZENE; /DIHYDRATE/ |
| Stability/Shelf Life | PROTECT FROM LIGHT; DARKENS ON EXPOSURE TO LIGHT /DIHYDRATE/ |
| Optical Rotation | Specific optical rotation: + 212 deg at 25 °C/D (alcohol); prisms; needles from water. /d-quinidine sulfate/ |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides/. |
| Refractive Index | INDEX OF REFRACTION ALPHA 1.565; BETA 1.607; GAMMA 1.670. OPTIC SIGN +, EXTINCTION PARALLEL, ELONGATION + |
| Other Experimental Properties | ODORLESS; VERY BITTER TASTE; SOLN ARE NEUTRAL OR ALKALINE TO LITMUS |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 746.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 746.33493574 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 746.33493574 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 174 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 53 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 538 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Quinidine Sulfate is the sulfate salt form of quinidine, an alkaloid with antimalarial and antiarrhythmic (Class la) properties. Quinidine sulfate exerts its anti-malarial activity by acting primarily as an intra-erythrocytic schizonticide through association with the hemepolymer (hemozoin) in the acidic food vacuole of the parasite thereby preventing further polymerization by heme polymerase enzyme. This results in accumulation of toxic heme and death of the parasite. Quinidine sulfate exerts its antiarrhythmic effects by depressing the flow of sodium ions into cells during phase 0 of the cardiac action potential, thereby slowing the impulse conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node, reducing the rate of phase 0 depolarization and prolonging the refractory period. Quinidine sulfate also reduces the slope of phase 4 depolarization in Purkinje-fibres resulting in slowed conduction and reduced automaticity in the heart.