CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 88.06 °C |
| Solubility | Complete |
| LogP | -2.1 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Hexahydrate, mp >250 °C/Foscarnet sodium/ |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 126.01 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 125.97181019 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 125.97181019 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 94.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 120 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
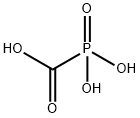
Phosphonoformic acid is phosphoric acid in which one of the hydroxy groups is replaced by a carboxylic acid group. It is used as the trisodium salt as an antiviral agent in the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis (CMV retinitis, an inflamation of the retina that can lead to blindness) and as an alternative to ganciclovir for AIDS patients who require concurrent antiretroviral therapy but are unable to tolerate ganciclovir due to haematological toxicity. It has a role as an antiviral drug, a sodium-dependent Pi-transporter inhibitor, a HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor and a geroprotector. It is a one-carbon compound, a member of phosphonic acids and a carboxylic acid. It is functionally related to a phosphonic acid and a formic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a phosphonatoformate and a phosphonoformate(2-).