298-00-0
Product Name:
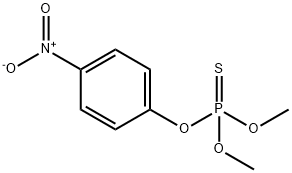
Parathion-methyl
Formula:
C8H10NO5PS
Synonyms:
O,O-Dimethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate;Methyl parathion
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Methyl parathion is a white crystalline solid which is often dissolved in a liquid solvent carrier. The commercial product is a tan liquid (xylene solution) with a pungent odor. It is slightly soluble to insoluble in water. Usually with the liquid solvent it is a combustible liquid. It is toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin absorption. It is used as an insecticide. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Crystals |
| Odor | Pungent, garlic-like odor |
| Boiling Point | 246 °F at 0.13 mmHg (NTP, 1992) |
| Melting Point | 99 to 100 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Flash Point | commercial product, containing xylene, has flashpoint of 115F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | less than 1 mg/mL at 73 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Density | 1.358 at 68 °F (EPA, 1998) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Density | 9.1 (NTP, 1992) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 9.7e-06 mmHg at 68 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| LogP | log Kow = 2.86 |
| Henry's Law Constant | Henry's Law constant = 1.0X10-7 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Hydrolyzes slowly in weak acid, rapidly in alkali |
| Autoignition Temperature | 120 °C (248 °F) /Methyl parathion 80% in xylene/ |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomp it emits very toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides, phosphorous oxides, and sulfur oxides/. |
| Odor Threshold | Odor Threshold Low: 0.0012 [mmHg] Odor threshold from AIHA |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.5367 at 25 °C/D |
| Dissociation Constants | pKa = 7.15 |
| Collision Cross Section | 149.84 Ų [M+H]+ 154.49 Ų [M-H]- |
| Kovats Retention Index | 1851 1878 1856 1905 1845 1852.2 1840.5 1843 1848.8 1857.6 1854.4 1872.5 1850.7 1847.7 1840 1855 1851 1848.4 1840 1895 1851 1855.2 1852.3 1864.8 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Light brown liquid /Technical product/ |
| Chemical Classes | Pesticides -> Organophosphate Insecticides |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 263.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 263.00173059 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 263.00173059 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 106 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 279 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Methyl parathion is an insecticide that does not occur naturally in the environment. Pure methyl parathion exists as white crystals. Impure methyl parathion is a brownish liquid that smells like rotten eggs.Methyl parathion is used to kill insects on farm crops, especially cotton. The EPA now restricts how methyl parathion can be used and applied; only trained people are allowed to spray it. Methyl parathion can no longer be used on food crops commonly consumed by children.
