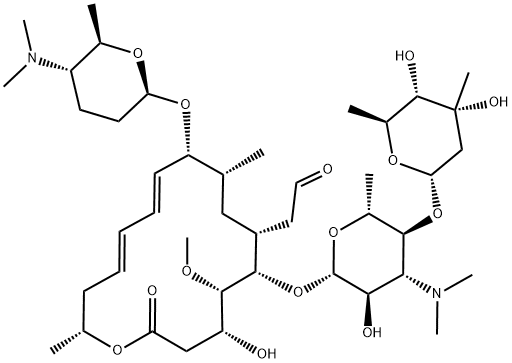
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Color/Form | Amorphous |
|---|---|
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in water |
| Optical Rotation | Specific optical rotation: -80 deg at 20 °C/D |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke & irritating fumes. |
| pH | Base |
| Other Experimental Properties | MW: 843.05. Crystals. MP: 134-137 °C. Specific optical rotation: -96 deg at 20 °C/D /Spiramycin I/ |
| Chemical Classes | Other Uses -> Pharmaceuticals |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 843.1 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 842.51400504 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 842.51400504 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 195 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 59 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1370 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 19 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Spiramycin is a macrolide originally discovered as product of Streptomyces ambofaciens, with antibacterial and antiparasitic activities. Although the specific mechanism of action has not been characterized, spiramycin likely inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. This agent also prevents placental transmission of toxoplasmosis presumably through a different mechanism, which has not yet been characterized.