2446-83-5
Product Name:
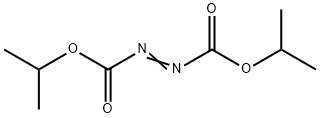
Diisopropyl azodicarboxylate
Formula:
C8H14N2O4
Synonyms:
DIAD;Diisopropyl azodiformate;Diisopropylazodicarboxylate
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Orange liquid; [Merck Index] Pungent odor; [Alfa Aesar MSDS] |
|---|---|
| Chemical Classes | Nitrogen Compounds -> Other Nitrogen Compounds |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Warning |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H351:Carcinogenicity H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 202.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 202.09535693 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 202.09535693 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 212 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
Description
Diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (DIAD) is the diisopropyl ester of azodicarboxylic acid. It is used as a reagent in the production of many organic compounds. It is often used in the Mitsunobu reaction, where it serves as an oxidizer of triphenylphosphine to triphenylphosphine oxide. It has also been used to generate aza-Baylis-Hillman adducts with acrylates. It can also serve as a selective deprotectant of N-benzyl groups in the presence of other protecting groups. Diisopropyl azodicarboxylate acted as a selective new precursor for synthesising oxime carbonates in high yields.
