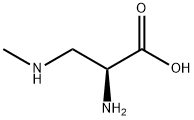
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Chemical Classes | other linear non-peptide (BMAA) |
|---|
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 118.13 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 118.074227566 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 118.074227566 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 75.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 8 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 84.1 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
L-BMAA is a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid that is L-alanine in which one of the methyl hydrogens is replaced by a methylamino group. A non-proteinogenic amino acid produced by cyanobacteria, it is a neurotoxin that has been postulated as a possible cause of neurodegenerative disorders of aging such as Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex (ALS-PDC) syndrome of Guam. It has a role as a neurotoxin and a bacterial metabolite. It is a secondary amino compound, a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid, a L-alanine derivative and a diamino acid.