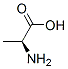
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Other Solid |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Orthorhombic crystals from water |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Sweet taste |
| Boiling Point | 250 °C (sublimes) |
| Melting Point | 300 dec °C |
| Solubility | 164000 mg/L (at 25 °C) |
| Density | 1.432 g/cu cm at 22 °C |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.00000011 [mmHg] |
| LogP | -2.85 |
| Optical Rotation | Specific optical rotation= +2.42 °For D-sodium line at 25 °C (c = 10 in H2O); +13.7 °For D sodium line at 25 °C (c = 2.063 in 6N HCl) |
| Ionization Efficiency | Positive |
| Dissociation Constants | 2.34 (at 25 °C) |
| Other Experimental Properties | PRISMS; DECOMP @ 204 °C /L-ALANINE HYDROCHLORIDE/ |
| Chemical Classes | Biological Agents -> Amino Acids and Derivatives |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 89.09 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 89.047678466 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 89.047678466 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 61.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
L-alanine is the L-enantiomer of alanine. It has a role as an EC 4.3.1.15 (diaminopropionate ammonia-lyase) inhibitor and a fundamental metabolite. It is a pyruvate family amino acid, a proteinogenic amino acid, a L-alpha-amino acid and an alanine. It is a conjugate base of a L-alaninium. It is a conjugate acid of a L-alaninate. It is an enantiomer of a D-alanine. It is a tautomer of a L-alanine zwitterion.