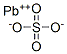CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Lead sulfate appears as a white crystalline solid. Insoluble in water and sinks in water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. May be mildly toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Used to make other chemicals. Use: in lithography, battery acid solution treated fabrics, used in varnishes. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | White, heavy crystal powder |
| Melting Point | 2138 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Solubility | In water, 0.0404 g/100 mL at 25 °C; slightly soluble in alkaline solutions. |
| Density | 6.2 at 68 °F (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes /of lead and sulfur oxides./ |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.877, 1.822, 1.894 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Lead is derived from the decay of radon. /Inorganic lead/ |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Lead Compounds, Inorganic |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 303 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 303.92838 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 303.92838 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 88.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 62.2 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Lead sulfate appears as a white crystalline solid. Insoluble in water and sinks in water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. May be mildly toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Used to make other chemicals. Use: in lithography, battery acid solution treated fabrics, used in varnishes.