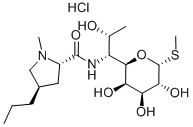
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Color/Form | Amorphous solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 187-190 |
| Solubility | freely soluble |
| LogP | 0.56 |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable in light and air. /Lincomycin HCl, USP/ |
| Optical Rotation | White or almost white crystalline powder, odorless or with a slight mercaptan-like odor and bitter taste, mp 156-158 °C. Specific optical rotation = +143 deg at 25 °C/D (water). pH of 1% aqueous solution = 4.8 /Lincomycin hydrochloride monohydrate/ |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of /oxides of sulfur and oxides of nitrogen/. |
| Ionization Efficiency | Negative |
| Dissociation Constants | pKa = 7.6 |
| Collision Cross Section | 201.8 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW] |
| Other Experimental Properties | Amorphous |
| Chemical Classes | Other Uses -> Pharmaceuticals |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 406.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 406.21375798 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 406.21375798 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 148 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 499 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 9 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Lincomycin is a carbohydrate-containing antibiotic produced by the actinomyces Streptomyces lincolnensis. It has a role as an antimicrobial agent and a bacterial metabolite. It is a carbohydrate-containing antibiotic, a S-glycosyl compound, a monocarboxylic acid amide, a pyrrolidinecarboxamide and a L-proline derivative.