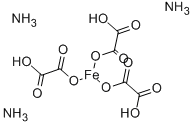
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Ferric ammonium oxalate appears as a green crystalline solid. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Used in making blueprints. |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.78 at 68 °F (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Affected by light /Hydrate/ |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /ammonia/. |
| Other Experimental Properties | Solid; yellowish-green; slight burnt sugar odor /Trihydrate/ |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Metals, Inorganic Compounds |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 374.02 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 373.977033 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 373.977033 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 244 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 60.5 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 7 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Ferric ammonium oxalate appears as a green crystalline solid. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Used in making blueprints.