CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Vapor Pressure | -1.49 ± 0.01 [log Psd at 298.15 K (Pa)] |
| Enthalpy of Sublimation | 85.4 ± 3.2 [ΔsubHb (kJ/mol) at 296.1-311.2 K] |
| Collision Cross Section | 127.46 Ų [M-H-CO2]- [CCS Type: DT; Buffer gas: N2; Dataset: PFAS] |
| Chemical Classes | PFAS |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P310:Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 330.05 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 3.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 14 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 329.97500367 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 329.97500367 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 383 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
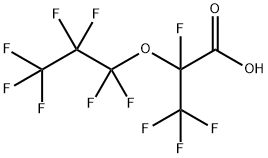
2,3,3,3-tetrafluoro-2-(heptafluoropropoxy)propanoic acid is a perfluorinated compound that is 2-propoxypentanoic acid in which all 11 of the hydrogens attached to carbon atoms have been replaced by fluorine atoms. Used as an alternative to perfluorooctanoic acid in the fluoropolymer industry for years, its widespread environmental distribution, high bioaccumulation capability, and human exposure have caused great concern, particularly as its potential toxicity and health risk is still largely unknown. It is a monocarboxylic acid, a perfluorinated compound and an ether.