121-19-7
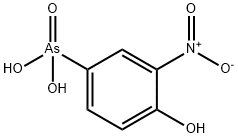
Product Name:
Roxarsone
Formula:
C6H6AsNO6
Synonyms:
2-Nitrophenol-4-arsonic acid;4-Hydroxy-3-nitrobenzenearsonic acid
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl arsonic acid appears as pale yellow crystals or light tan powder. (NTP, 1992) |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Tufts of pale-yellow needles or rhombohedral plates from water |
| Melting Point | greater than 572 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Solubility | less than 1 mg/mL at 73 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides & arsenic/. |
| Collision Cross Section | 145.5 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards] |
| Other Experimental Properties | Puffs up and deflagrates on heating |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Arsenic Compounds, Organic |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 263.04 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 262.941106 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 262.941106 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 124 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 270 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl arsonic acid appears as pale yellow crystals or light tan powder. (NTP, 1992)
