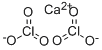CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Calcium chlorate appears as a white crystalline solid. It forms a very flammable mixture with combustible materials and this mixture may be explosive if the combustible material is finely divided. The mixture can be ignited by friction. Contact with strong sulfuric acid can cause fires or explosions. When mixed with ammonium salts, spontaneous decomposition and ignition may result. Prolonged exposure of the material to fire or heat can result in an explosion. It is used in photography, in pyrotechnics, and as a herbicide. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | White crystals |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Melting Point | 644 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Solubility | 197 g/100 g water at 25 °C |
| Density | 2.71 at 32 °F (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /hydrogen chloride/. |
| Other Experimental Properties | Powerful oxidant |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Metals, Inorganic Compounds |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 206.98 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 205.8697840 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 205.8697840 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 114 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 36.5 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Calcium chlorate appears as a white crystalline solid. It forms a very flammable mixture with combustible materials and this mixture may be explosive if the combustible material is finely divided. The mixture can be ignited by friction. Contact with strong sulfuric acid can cause fires or explosions. When mixed with ammonium salts, spontaneous decomposition and ignition may result. Prolonged exposure of the material to fire or heat can result in an explosion. It is used in photography, in pyrotechnics, and as a herbicide.