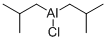CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Colorless liquid |
| Boiling Point | 108 °C @ 0.13 kPa |
| Melting Point | -40 °C |
| Density | 0.9118 g/mL @ 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Low melting solids or colorless, volatile liquids. /Alkylaluminum halides/ |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition ... emits toxic fumes of /hydrogen chloride/. |
| Other Experimental Properties | Freezing point: -39.5 °C |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Metals, Organic Compounds |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H250:Pyrophoric liquids; Pyrorophoric solids H261:Substances And Mixtures Which, In Contact With Water,Emit Flammable Gases H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P231+P232:Handle under inert gas. Protect from moisture. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 176.66 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 176.0912417 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 176.0912417 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 10 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 71.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Bis(isobutyl)aluminum chloride is an organoaluminum compound. Aluminum is the most abundant metal in the earth's crust and is always found combined with other elements such as oxygen, silicon, and fluorine. (L739, L740)