Triisobutyl phosphate
Synonym(s):Triisobutyl phosphate
- CAS NO.:126-71-6
- Empirical Formula: C12H27O4P
- Molecular Weight: 266.31
- MDL number: MFCD00039849
- EINECS: 204-798-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-05-13 18:00:15
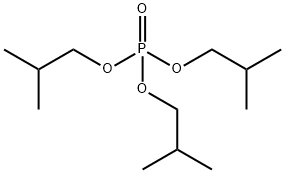
What is Triisobutyl phosphate?
Description
Advances in technological development over the last couple of centuries have led to the use of synthetic carbon-based polymers for everyday household and office items, where once wood or metal were desired. The high fuel values for some of these materials could pose danger where risk of combustion is high; therefore, flame retardants have been introduced into and coating for electronic devices. These substances have a broad application field and good fire safety performance.
The Uses of Triisobutyl phosphate
Phosphate esters are used as flame retardants, plasticizers,
hydraulic fluids, solvents, extraction agents, antifoam agents,
Partition behavior in water, sediment, and soil
Phosphate ester flame retardants enter the environment from
industrial sources and disposal of consumer products containing
flame retardants. These anthropogenic compounds
have been detected in water, soil, and air owing to widespread
use following their fast emergence and popularization during
1970s. Occurrence of these phosphate ester flame retardants is
widespread in surface water and groundwater because of the
leaching of PVC plastics and polyurethane foams, effluent from
industrial sources, and spills of hydraulic fluids. This primary
contaminated water is then transported to a secondary source,
such as drinking water. Hydrolysis, although slow because of
poor solubility and pH dependence, is the most important
abiotic elimination process. In soil and sediment, phosphate
ester flame retardants are persistent because they have the
tendency to adsorb strongly. Volatilization and biodegradation
are potential elimination processes for phosphate esters
adsorbed to soil.
Environmental persistency (degradation/speciation)
These retardants can change chemical composition in the
environment. Generally, most phosphate esters are poorly
soluble in water and adsorb strongly to soils. These compounds
are considered emerging pollutants because of their prevalence
and persistence in the environment. Particulate-phase phosphate
esters are subject to wet and dry deposition, whereas
semi-volatile phosphate esters have the potential to hydrolyze
to diesters, monoesters, and phosphoric acid. There is no
information available that suggests that selected phosphate
ester flame retardants undergo transformation or degradation
in the atmosphere.
Long-range transport
This is highly dependent on the specific compound.
Bioaccumulation and biomagnification
Phosphate esters are subject to biodegradation in aquatic and
terrestrial environments.
Properties of Triisobutyl phosphate
| Boiling point: | ~205 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.965 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
| Flash point: | 150 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 0.26g/l |
| form | Oil |
| color | Colourless |
| Water Solubility | 264mg/L at 25℃ |
Safety information for Triisobutyl phosphate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Triisobutyl phosphate
| InChIKey | HRKAMJBPFPHCSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
Sagar Speciality Chemicals Private Limited
New Products
3-N-BOC-(S)-AMINO BUTYRONITRILE 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 4-Acetyl-2-methylbenzoicacid Acetyl-meldrum's acid Ethyl-4-Pyrazole carboxylate 2,6 Di acetylpyridine 2,6-Pyridinedimethanol 5,7-Dichloro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine 5-Bromo-2-Methoxy-4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Iodopyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine 2-Chloro-3-Bromo-5-Amiopyridine METHYL-4-(BUTYRYLAMINO)3-METHYL-5-NITROBENZOATE TRANS-CYCLOBUTANE-1,2- DICARBOXYLIC ACID 5-Nitro indazole R-(-)-5-(2-AMINO-PROPYL)-2-METHOXY-BENZENESULFONAMIDE 1,3-cyclohexanedione 4-Aminophenaethylalchol 3-NITRO-5-ACETYL IMINODIBENZYL (S)-(+)-4-BENZYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE 4-FLUORO PHENYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 1.0 M IN THF 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL6-(2,4,4-TRI METHYL PHENYL)-2-PYRIDONE MONO ETHANOL AMINE(PIROCTONE OLAMINE)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 126-71-6 Tri Isobutyl Phosphate 98%View Details
126-71-6 Tri Isobutyl Phosphate 98%View Details
126-71-6 -
 126-71-6 98%View Details
126-71-6 98%View Details
126-71-6 -
 68915-31-1 99%View Details
68915-31-1 99%View Details
68915-31-1 -
 Azadirachtin 11141-17-6 99%View Details
Azadirachtin 11141-17-6 99%View Details
11141-17-6 -
 26062-79-3 99%View Details
26062-79-3 99%View Details
26062-79-3 -
 Geraniol 99%View Details
Geraniol 99%View Details
106-24-1 -
 BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
8001-54-5 -
 Amrit Neem 11141-17-6 99%View Details
Amrit Neem 11141-17-6 99%View Details
11141-17-6