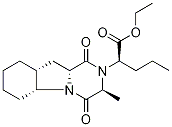
Perindopril
- CAS NO.:82834-16-0
- Empirical Formula: C19H32N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 368.47
- MDL number: MFCD00865859
- EINECS: 617-394-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-18 11:31:19
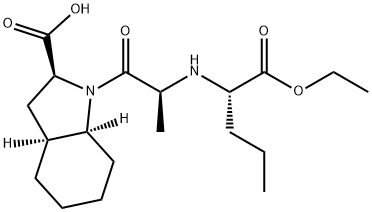
What is Perindopril?
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed with peak plasma concentrations occurring approximately 1 hour after oral administration. Bioavailability is 65-75%. Following absorption, perindopril is hydrolyzed to perindoprilat, which has an average bioavailability of 20%. The rate and extent of absorption is unaffected by food. However, food decreases the extent of biotransformation to peridoprilat and reduces its bioavailability by 35%.
Toxicity
The most likely symptom of overdose is severe hypotension. The most common adverse effects observed in controlled clinical trials include cough, digestive symptoms, fatigue, headache, and dizziness.
Description
Perindopril is a potent, orally-active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor useful in the management of hypertension. Against rat ACE, perindopril appears to be more potent than enalapril and enalaprilat, and is approximately equipotent to rarnipril (HOE 498). Its long duration of action suggests the possibility of once-daily dosing.
Description
Perindopril is a long-acting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor that is used to treat cardiovascular conditions. It is commercially available as arginine and tert-butylamine (also known as erbumine) salts. This year, M. Teresa Duarte and her colleagues in Portugal used single-crystal X-ray diffraction spectroscopy to determine the structures of two perindopril erbumine polymorphs and a previously unknown hydrated form.
The Uses of Perindopril
Labeled Perindopril, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Perindopril by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
What are the applications of Application
Perindopril is an ACE inhibitor
Background
Perindopril is a nonsulfhydryl prodrug that belongs to the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor class of medications. It is rapidly metabolized in the liver to perindoprilat, its active metabolite, following oral administration. Perindoprilat is a potent, competitive inhibitor of ACE, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of angiotensin I (ATI) to angiotensin II (ATII). ATII regulates blood pressure and is a key component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Perindopril may be used to treat mild to moderate essential hypertension, mild to moderate congestive heart failure, and to reduce the cardiovascular risk of individuals with hypertension or post-myocardial infarction and stable coronary disease.
Indications
For the treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension, mild to moderate congestive heart failure, and to reduce the cardiovascular risk of individuals with hypertension or post-myocardial infarction and stable coronary disease.
Pharmacokinetics
Perindopril is a nonsulfhydryl prodrug that is metabolized via first pass effect (62%) and systemic hydrolysis (38%) to perindoprilat, its active metabolite, following oral administration. Perindoprilat lowers blood pressure by antagonizing the effect of the RAAS. The RAAS is a homeostatic mechanism for regulating hemodynamics, water and electrolyte balance. During sympathetic stimulation or when renal blood pressure or blood flow is reduced, renin is released from the granular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidneys. In the blood stream, renin cleaves circulating angiotensinogen to ATI, which is subsequently cleaved to ATII by ACE. ATII increases blood pressure using a number of mechanisms. First, it stimulates the secretion of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. Aldosterone travels to the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting tubule of nephrons where it increases sodium and water reabsorption by increasing the number of sodium channels and sodium-potassium ATPases on cell membranes. Second, ATII stimulates the secretion of vasopressin (also known as antidiuretic hormone or ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland. ADH stimulates further water reabsorption from the kidneys via insertion of aquaporin-2 channels on the apical surface of cells of the DCT and collecting tubules. Third, ATII increases blood pressure through direct arterial vasoconstriction. Stimulation of the Type 1 ATII receptor on vascular smooth muscle cells leads to a cascade of events resulting in myocyte contraction and vasoconstriction. In addition to these major effects, ATII induces the thirst response via stimulation of hypothalamic neurons. ACE inhibitors inhibit the rapid conversion of ATI to ATII and antagonize RAAS-induced increases in blood pressure. ACE (also known as kininase II) is also involved in the enzymatic deactivation of bradykinin, a vasodilator. Inhibiting the deactivation of bradykinin increases bradykinin levels and may sustain the effects of perindoprilat by causing increased vasodilation and decreased blood pressure.
Metabolism
Extensively metabolized, with only 4-12% of the dose recovered in urine following oral administration. Six metabolites have been identified: perindoprilat, perindopril glucuronide, perindoprilat glucuronide, a perindopril lactam, and two perindoprilat lactams. Only perindoprilat is pharmacologically active. Peridoprilat and perindoprilat glucuronide are the two main circulating metabolites.
Properties of Perindopril
| Melting point: | 100-101°C |
| Boiling point: | 537.4±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.150±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Perindopril
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Perindopril
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
3-N-BOC-(S)-AMINO BUTYRONITRILE 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 4-Acetyl-2-methylbenzoicacid Acetyl-meldrum's acid Ethyl-4-Pyrazole carboxylate 2,6 Di acetylpyridine 2,6-Pyridinedimethanol 5,7-Dichloro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine 5-Bromo-2-Methoxy-4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Iodopyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine 2-Chloro-3-Bromo-5-Amiopyridine METHYL-4-(BUTYRYLAMINO)3-METHYL-5-NITROBENZOATE TRANS-CYCLOBUTANE-1,2- DICARBOXYLIC ACID 5-Nitro indazole R-(-)-5-(2-AMINO-PROPYL)-2-METHOXY-BENZENESULFONAMIDE 1,3-cyclohexanedione 4-Aminophenaethylalchol (S)-(+)-4-BENZYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE 3-NITRO-5-ACETYL IMINODIBENZYL 4-FLUORO PHENYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 1.0 M IN THF 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL6-(2,4,4-TRI METHYL PHENYL)-2-PYRIDONE MONO ETHANOL AMINE(PIROCTONE OLAMINE)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
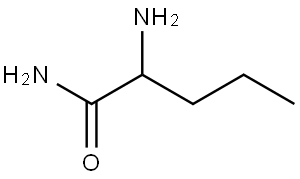
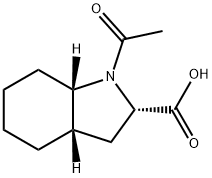
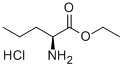
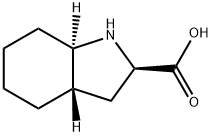
You may like
-
 82834-16-0 Perindopril 98%View Details
82834-16-0 Perindopril 98%View Details
82834-16-0 -
 Perindopril 97%View Details
Perindopril 97%View Details -
 2,3 Dichloro-4-Hydroxy Aniline 39183-17-0 99%View Details
2,3 Dichloro-4-Hydroxy Aniline 39183-17-0 99%View Details
39183-17-0 -
 17673-56-2 99%View Details
17673-56-2 99%View Details
17673-56-2 -
 13463-67-7 Titanium Dioxide 99%View Details
13463-67-7 Titanium Dioxide 99%View Details
13463-67-7 -
 143-07-7 99%View Details
143-07-7 99%View Details
143-07-7 -
 20776-67-4 99%View Details
20776-67-4 99%View Details
20776-67-4 -
 acid blue 113, acid navy blue , wool navy blue 0View Details
acid blue 113, acid navy blue , wool navy blue 0View Details
3351-05-1