Mycophenolate mofetil
- CAS NO.:128794-94-5
- Empirical Formula: C23H31NO7
- Molecular Weight: 433.49
- MDL number: MFCD00867568
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-11-16 20:18:48
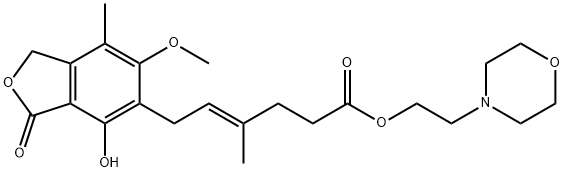
What is Mycophenolate mofetil?
Absorption
Mycophenolate mofetil is rapidly absorbed in the small intestine. The maximum concentration of its active metabolite, MPA, is attained 60 to 90 minutes following an oral dose. The average bioavailability of orally administered mycophenolate mofetil in a pharmacokinetic study of 12 healthy patients was 94%. In healthy volunteers, the Cmax of mycophenolate mofetil was 24.5 (±9.5)μg/mL. In renal transplant patients 5 days post-transplant, Cmax was 12.0 (±3.82) μg/mL, increasing to 24.1 (±12.1)μg/mL 3 months after transplantation. AUC values were 63.9 (±16.2) μg?h/mL in healthy volunteers after one dose, and 40.8 (±11.4) μg?h/mL, and 65.3 (±35.4)μg?h/mL 5 days and 3 months after a renal transplant, respectively. The absorption of mycophenolate mofetil is not affected by food.
Toxicity
LD50
The LD50 of oral mycophenolate mofetil in rats is 250 mg/kg and >4000 mg/kg in mice.
Overdose information
Possible signs and symptoms of acute overdose may consist of hematological abnormalities including leukopenia and neutropenia, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Description
Mycophenolate mofetil was launched in 1995 in the U.S.A., its first market worldwide, for the prevention of acute kidney transplant rejection in conjunction with other immunosuppressive therapy and to treat refractory acute kidney graft rejection. With improved oral absorption and bioavailability, mycophenolate mofetil is a prodrug of mycophenolic acid (MPA), a fermentation product of several Penicillium species. MPA is a selective, reversible, non-competitive inhibitor of inosinate dehydrogenase and guanylate synthetase. It inhibits the de now pathway of purine biosynthesis. MPA was found to have more potent antiproliferative effects on T and B lymphocytes than other cell types. Compared with other immunosuppressants, mycophenolate mofetil is reportedly superior due to its unique mechanism of action and excellent safety profile for long term use. Mycophenolate mofetil is being investigated clinically in the treatment of heart and liver transplantation rejection, asthma, in preventing coronary artery restenosis, and in treating rheumatoid arthritis.
The Uses of Mycophenolate mofetil
For the prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving allogeneic renal, cardiac or hepatic transplants. Mycophenolate mofetil should be used concomitantly with cyclosporine and corticosteroids.
Indications
Mycophenolate mofetil is indicated in combination with other immunosuppressants to prevent the rejection of kidney, heart, or liver transplants in adult and pediatric patients ≥3 months old. Mycophenolate mofetil may also be used off-label as a second-line treatment for autoimmune hepatitis that has not responded adequately to first-line therapy. Other off-label uses of this drug include lupus-associated nephritis and dermatitis in children.
Background
Mycophenolate mofetil, also known as MMF or CellCept, is a prodrug of mycophenolic acid, and classified as a reversible inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH). This drug is an immunosuppressant combined with drugs such as Cyclosporine and corticosteroids to prevent organ rejection after hepatic, renal, and cardiac transplants. It is marketed by Roche Pharmaceuticals and was granted FDA approval for the prophylaxis of transplant rejection in 1995. In addition to the above uses, mycophenolate mofetil has also been studied for the treatment of nephritis and other complications of autoimmune diseases. Unlike another immunosuppressant class, the calcineurin inhibitors, MMF generally does not cause nephrotoxicity or fibrosis.
Previously, mycophenolic acid (MPA) was administered to individuals with autoimmune diseases beginning in the 1970s, but was discontinued due to gastrointestinal effects and concerns over carcinogenicity. The new semi-synthetic 2-morpholinoethyl ester of MPA was synthesized to avoid the gastrointestinal effects associated with the administration of MPA. It demonstrates an increased bioavailability, a higher efficacy, and reduced gastrointestinal effects when compared to MPA.
What are the applications of Application
Mycophenolate mofetil is a compound that suppresses T-lymphocytic and antibody responses
Pharmacokinetics
Mycophenolate mofetil is a prodrug of mycophenolic acid (MPA). The active form of mycophenolate, MPA, prevents the proliferation of immune cells and the formation of antibodies that cause transplant rejection. The above effects lead to higher rates of successful transplantation, avoiding the devastating effects of graft rejection.
Metabolism
After both oral and intravenous administration mycophenolate mofetil is entirely metabolized by liver carboxylesterases 1 and 2 to mycophenolic acid (MPA), the active parent drug. It is then metabolized by the enzyme glucuronyl transferase, producing the inactive phenolic glucuronide of MPA (MPAG). The glucuronide metabolite is important, as it is then converted to MPA through enterohepatic recirculation. Mycophenolate mofetil that escapes metabolism in the intestine enters the liver via the portal vein and is transformed to pharmacologically active MPA in the liver cells.N-(2-carboxymethyl)-morpholine, N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-morpholine, and the N-oxide portion of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-morpholine are additional metabolites of MMF occurring in the intestine as a result of liver carboxylesterase 2 activity. UGT1A9 and UGT2B7 in the liver are the major enzymes contributing to the metabolism of MPA in addition to other UGT enzymes, which also play a role in MPA metabolism. The four major metabolites of MPA are 7-O-MPA-β-glucuronide (MPAG, inactive), MPA acyl-glucuronide (AcMPAG), produced by uridine 5?-diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases (UGT) activities, 7-O-MPA glucoside produced via UGT, and small amounts 6-O-des-methyl-MPA (DM-MPA) via CYP3A4/5 and CYP2C8 enzymes.
Properties of Mycophenolate mofetil
| Melting point: | 95-96°C |
| Boiling point: | 637.6±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.222±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥15mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
Safety information for Mycophenolate mofetil
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Mycophenolate mofetil
| InChIKey | RTGDFNSFWBGLEC-SYZQJQIISA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
ChemBioReas Life Sciences
KARPSCHEM LABORATORIES PVT. LTD.
New Products
3-N-BOC-(S)-AMINO BUTYRONITRILE 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 4-Acetyl-2-methylbenzoicacid Acetyl-meldrum's acid Ethyl-4-Pyrazole carboxylate 2,6 Di acetylpyridine 2,6-Pyridinedimethanol 5,7-Dichloro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine 5-Bromo-2-Methoxy-4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Iodopyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine 2-Chloro-3-Bromo-5-Amiopyridine METHYL-4-(BUTYRYLAMINO)3-METHYL-5-NITROBENZOATE TRANS-CYCLOBUTANE-1,2- DICARBOXYLIC ACID 5-Nitro indazole R-(-)-5-(2-AMINO-PROPYL)-2-METHOXY-BENZENESULFONAMIDE 1,3-cyclohexanedione 4-Aminophenaethylalchol (S)-(+)-4-BENZYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE 3-NITRO-5-ACETYL IMINODIBENZYL 4-FLUORO PHENYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 1.0 M IN THF 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL6-(2,4,4-TRI METHYL PHENYL)-2-PYRIDONE MONO ETHANOL AMINE(PIROCTONE OLAMINE)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 128794-94-5 MycophenolateMofetil 98%View Details
128794-94-5 MycophenolateMofetil 98%View Details
128794-94-5 -
 128794-94-5 96%View Details
128794-94-5 96%View Details
128794-94-5 -
 2,3 Dichloro-4-Hydroxy Aniline 39183-17-0 99%View Details
2,3 Dichloro-4-Hydroxy Aniline 39183-17-0 99%View Details
39183-17-0 -
 17673-56-2 99%View Details
17673-56-2 99%View Details
17673-56-2 -
 13463-67-7 Titanium Dioxide 99%View Details
13463-67-7 Titanium Dioxide 99%View Details
13463-67-7 -
 143-07-7 99%View Details
143-07-7 99%View Details
143-07-7 -
 20776-67-4 99%View Details
20776-67-4 99%View Details
20776-67-4 -
 acid blue 113, acid navy blue , wool navy blue 0View Details
acid blue 113, acid navy blue , wool navy blue 0View Details
3351-05-1