Lopinavir
Synonym(s):(αS)-N-[(1S,3S,4S)-4-[[(2,6-Dimethylphenoxy)acetyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1-(phenylmethyl)pentyl]tetrahydro-α-(1-methylethyl)-2-oxo-1(2H)-;Lopinavir
- CAS NO.:192725-17-0
- Empirical Formula: C37H48N4O5
- Molecular Weight: 628.81
- MDL number: MFCD22628840
- EINECS: 200-001-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-06-30 15:45:59
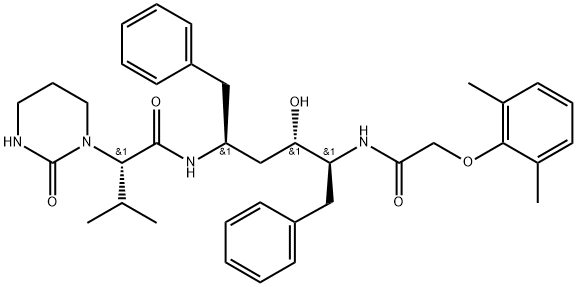
What is Lopinavir?
Absorption
When administered alone, lopinavir has exceptionally low oral bioavailability (~25%) - for this reason, it is exclusively co-administered with ritonavir, which dramatically improves bioavailability, hinders drug metabolism, and allows for the attainment of therapeutic lopinavir concentrations. Following oral administration of lopinavir/ritonavir, maximal plasma concentrations are achieved at approximately 4.4 hours (Tmax), and the Cmax and AUCtau are 9.8 ± 3.7 - 11.8 ± 3.7 μg/mL and 92.6 ± 36.7 - 154.1 ± 61.4 μg?h/mL, respectively.
Relative to administration in the fasted state, administration with a meal increases the AUC of the tablet formulation slightly (~19%) but dramatically increases the AUC of the oral solution formulation (~130%).
Toxicity
As lopinavir is only available in combination with ritonavir, experience with acute lopinavir overdose in isolation is limited. The risk related to overdose appears more pronounced in pediatric patients. One case report detailed a fatal cardiogenic shock in a 2.1kg infant following an approximately 10-fold overdose of Kaletra oral solution, while other reported reactions to overdose in infants include complete AV block, cardiomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and acute renal failure. The oral Kaletra solution is highly concentrated, posing a greater risk of overdose, and contains approximately 42% (v/v) ethanol, further increasing risk in children and infants.
There is no antidote for lopinavir overdose. Treatment of overdose should consist largely of supportive measures and close observation of vital signs and clinical status of the affected patient. Consideration should be given to the removal of unabsorbed drug using gastric lavage or activated charcoal, if clinically indicated. Dialysis is unlikely to be of benefit as lopinavir is highly protein-bound, but may help to remove ethanol and propylene glycol from the circulation in the case of overdose with Kaletra oral solution.
Description
Lopinavir, the sixth HIV protease inhibitor in the “navir” class, was launched in coformulation with ritonavir, another HIV protease inhibitor already marketed (Abbott, 1996); this original formulation was introduced as Kaletra for use in combination with either nucleoside or non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors for the treatment of AIDS in adults and children. Lopinavir is a peptidomimetic compound with a structural core identical to that of ritonavir, on which terminal groups, particularly a modified valine, were introduced by peptide coupling procedures. Lopinavir is a potent competitive inhibitor of HIV-I protease exhibiting high potential against ritonavir-resistant mutations. In several animal species, pharmacokinetic studies with the lopinavirlritonavir association showed that the modest properties of lopinavir were significantly improved in presence of ritonavir, in terms of Cmax and duration of action. Ritonavir inhibits the P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4 and the human liver microsomal metabolism of lopinavir, so strongly amplifying plasma levels of this latter component. In AIDS patients, the plasma HIV RNA level was considerably reduced and the CD4+ T-cell counts increased after administration of lopinavir combined with relatively small doses of ritonavir. Kaletra is intended to be used jointly with other antiretroviral agents.
The Uses of Lopinavir
Lopinavir is a potent HIV protease inhibitor with Ki of 1.3 pM
Indications
The combination product lopinavir/ritonavir, marketed under the brand name Kaletra, is indicated in combination with other antiretrovirals for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients ≥14 days old.
Background
Lopinavir is an antiretroviral protease inhibitor used in combination with other antiretrovirals in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Lopinavir is marketed and administered exclusively in combination with ritonavir - this combination, first marketed by Abbott under the brand name Kaletra in 2000, is necessary due to lopinavir's poor oral bioavailability and extensive biotransformation. Ritonavir is a potent inhibitor of the enzymes responsible for lopinavir metabolism, and its co-administration "boosts" lopinavir exposure and improves antiviral activity. Like many other protease inhibitors (e.g. saquinavir, nelfinavir), lopinavir is a peptidomimetic molecule - it contains a hydroxyethylene scaffold that mimics the peptide linkage typically targeted by the HIV-1 protease enzyme but which itself cannot be cleaved, thus preventing the activity of the HIV-1 protease.
Lopinavir was previously under investigation in combination with ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2.
What are the applications of Application
Lopinavir is an HIV-1 protease inhibitor
Pharmacokinetics
Lopinavir inhibits the activity of an enzyme critical for the HIV viral lifecycle. It has a moderate duration of action necessitating once or twice daily dosing. Lopinavir, like other protease inhibitors, has a propensity for participating in drug interactions - use caution when administering lopinavir to patients maintained on other pharmaceutical agents as pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interactions are common. Fatal hepatotoxicity and pancreatitis have been noted in patients undergoing therapy with lopinavir and patients with an increased baseline risk of these events should be monitored closely throughout therapy.
Metabolism
Lopinavir undergoes extensive oxidative metabolism, almost exclusively via hepatic CYP3A isozymes. Co-administration with ritonavir, a potent inhibitor of CYP3A enzymes, helps to stave off lopinavir's biotransformation and increase plasma levels of active antiviral drug. Twelve metabolites have been identified in vitro, with the C-4 oxidation products M1, M3, and M4 being the predominant metabolites found in plasma. The structures of these primary metabolites have been identified, but precise structural information regarding the remaining minor metabolites has not been elucidated.
Properties of Lopinavir
| Melting point: | 255.2-260.6 °F (124—127°C) |
| Boiling point: | 924.1±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.163±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble20mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
Safety information for Lopinavir
Computed Descriptors for Lopinavir
Abamectin manufacturer
TYNDAL LABS PVT LTD
Venture Pharmaceuticals pvt ltd
HRV Global Life Sciences
New Products
3-N-BOC-(S)-AMINO BUTYRONITRILE 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 4-Acetyl-2-methylbenzoicacid Acetyl-meldrum's acid Ethyl-4-Pyrazole carboxylate 2,6 Di acetylpyridine 2,6-Pyridinedimethanol 5,7-Dichloro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine 5-Bromo-2-Methoxy-4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Iodopyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine 2-Chloro-3-Bromo-5-Amiopyridine METHYL-4-(BUTYRYLAMINO)3-METHYL-5-NITROBENZOATE TRANS-CYCLOBUTANE-1,2- DICARBOXYLIC ACID 5-Nitro indazole R-(-)-5-(2-AMINO-PROPYL)-2-METHOXY-BENZENESULFONAMIDE 1,3-cyclohexanedione 4-Aminophenaethylalchol (S)-(+)-4-BENZYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE 3-NITRO-5-ACETYL IMINODIBENZYL 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL6-(2,4,4-TRI METHYL PHENYL)-2-PYRIDONE MONO ETHANOL AMINE(PIROCTONE OLAMINE) 4-FLUORO PHENYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 1.0 M IN THFRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 LOPINAVIR 99%View Details
LOPINAVIR 99%View Details
192725-17-0 -
 192725-17-0 Lopinavir 98%View Details
192725-17-0 Lopinavir 98%View Details
192725-17-0 -
 192725-17-0 98%View Details
192725-17-0 98%View Details
192725-17-0 -
 Lopinavir 192725-17-0 98%View Details
Lopinavir 192725-17-0 98%View Details
192725-17-0 -
 192725-17-0 Lopinavir 99%View Details
192725-17-0 Lopinavir 99%View Details
192725-17-0 -
 192725-17-0 98%View Details
192725-17-0 98%View Details
192725-17-0 -
 Lopinavir 98%View Details
Lopinavir 98%View Details
192725-17-0 -
 Lopinavir 98%View Details
Lopinavir 98%View Details
192725-17-0