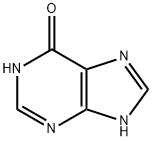
Inosine
Synonym(s):(−)-Inosine;Hypoxanthine 9-β-D -ribofuranoside;Hypoxanthine Riboside;Inosine;Inosine - CAS 58-63-9 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:58-63-9
- Empirical Formula: C10H12N4O5
- Molecular Weight: 268.23
- MDL number: MFCD00066770
- EINECS: 200-390-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-04-24 17:21:45
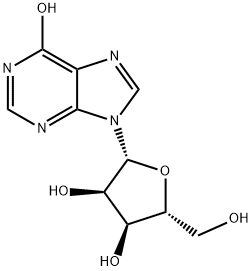
What is Inosine?
Description
Inosine is a natural purine nucleoside that commonly occurs in transfer RNAs in humans. The molecule consists of hypoxanthine connected to a ribofuranose ring via a glycosidic bond. It is a degradation product of adenosine.
Elsewhere in nature, inosine is found in red meat, pork, and poultry. Its 5’-monophosphate is associated with the flavor and taste of red and white meats.
In 1910 chemists Phoebus A.T. Levene and Walter A. Jacobs at the Rockefeller Institute of Medical Research in New York City (now Rockefeller University) synthesized inosine by treating adenosine with sodium nitrate and acetic acid. Later (in 1947), using less harsh conditions, Herman M. Kalckar at the Public Health Institute of the City of New York prepared inosine by incubating adenosine with intestine-based adenosine deaminase.
Since 2000, inosine has been tried as a treatment for medical conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, stroke, and spinal cord injuries. None of these efforts produced a commercial drug. But earlier this year, inosine turned up in an off-target result generated by a CRISPR-based gene editor.
David R. Liu and collaborators at the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT (Cambridge, MA) and Harvard University found that an adenine base editor (ABE) that efficiently converts targeted A–T base pairs in genomic DNA to G–C pairs does not do so well when it edits cellular RNAs. The editor, called ABEmax, generates a low but significant amount of inosine from the adenosine in RNA. The authors do not know whether the error will have any biological effects. But they note that some cancers evaded immune checkpoint inhibitors when similar results occurred in other RNA studies.
The Uses of Inosine
Inosine has been used:
- as a medium supplement in nucleotide rescue experiments in pancreatic cancer cell lines.
- as a component in holidic (synthetic) medium and in larval two-choice preference assay.
- as a reference standard in mass spectroscopy.
What are the applications of Application
Inosine is a metabolite of adenosine that acts as a potent coronary vasodilator
Properties of Inosine
| Melting point: | 222-226 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 226 C (dec.) |
| Density | 1.3846 (rough estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | H2O: 0.5 M, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | 2.1 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
Safety information for Inosine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Inosine
| InChIKey | UGQMRVRMYYASKQ-PKJMTWSGSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
3-N-BOC-(S)-AMINO BUTYRONITRILE 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 4-Acetyl-2-methylbenzoicacid Acetyl-meldrum's acid Ethyl-4-Pyrazole carboxylate 2,6 Di acetylpyridine 2,6-Pyridinedimethanol 5,7-Dichloro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine 5-Bromo-2-Methoxy-4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Iodopyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine 2-Chloro-3-Bromo-5-Amiopyridine METHYL-4-(BUTYRYLAMINO)3-METHYL-5-NITROBENZOATE TRANS-CYCLOBUTANE-1,2- DICARBOXYLIC ACID 5-Nitro indazole R-(-)-5-(2-AMINO-PROPYL)-2-METHOXY-BENZENESULFONAMIDE 1,3-cyclohexanedione 4-Aminophenaethylalchol 3-NITRO-5-ACETYL IMINODIBENZYL (S)-(+)-4-BENZYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE 4-FLUORO PHENYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 1.0 M IN THF 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL6-(2,4,4-TRI METHYL PHENYL)-2-PYRIDONE MONO ETHANOL AMINE(PIROCTONE OLAMINE)Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 58-63-9 Inosine, 98% 99%View Details
58-63-9 Inosine, 98% 99%View Details
58-63-9 -
 Inosine 58-63-9 99%View Details
Inosine 58-63-9 99%View Details
58-63-9 -
 68915-31-1 99%View Details
68915-31-1 99%View Details
68915-31-1 -
 Azadirachtin 11141-17-6 99%View Details
Azadirachtin 11141-17-6 99%View Details
11141-17-6 -
 26062-79-3 99%View Details
26062-79-3 99%View Details
26062-79-3 -
 Geraniol 99%View Details
Geraniol 99%View Details
106-24-1 -
 BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
8001-54-5 -
 Amrit Neem 11141-17-6 99%View Details
Amrit Neem 11141-17-6 99%View Details
11141-17-6