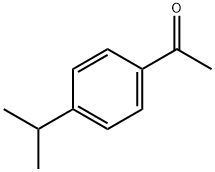
Cuminaldehyde
Synonym(s):4-Isopropylbenzaldehyde
- CAS NO.:122-03-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H12O
- Molecular Weight: 148.2
- MDL number: MFCD00006953
- EINECS: 204-516-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-15 08:42:14
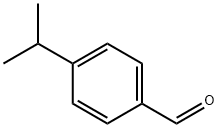
What is Cuminaldehyde?
Description
November is flavor and aroma month!
Cuminaldehyde, an aromatic aldehyde, gets its name from one of its main natural sources: the cumin plant (Cuminum cyminum) that grows in countries from Turkey across to India. In addition to cumin, cuminaldehyde is found in the essential oils of eucalyptus, myrrh, and cassia.
In small amounts, cuminaldehyde has a pleasant, herbal aroma; however, it also has an acrid, burning taste. As the hazard information table shows, direct exposure can have some unpleasant consequences.
Cumin has been used as a flavoring agent for centuries; cuminaldehyde has been in the chemical literature since at least the 1880s. In volume 2 (1880) of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (then called the American Chemical Journal), an abstract of an article about derivatives of stilbene (1,2-diphenylethylene) describes a reaction between “cumic aldehyde” and phenylacetic acid to form isopropylstilbene.
Almost 70 years later, Nathan N. Crounse at the Hilton-Davis Chemical Co. (Cincinnati) reported a synthesis of cuminaldehyde that uses the high-pressure Gattermann–Koch reaction to formylate cumene (isopropylbenzene) with carbon monoxide. The aldehyde can also be prepared by the reduction of p-isopropylbenzoyl chloride.
Today, most commercial cuminaldehyde is synthetic. It is sold as an ingredient for flavoring agents, perfumes, and other aroma-containing products. It also has several purported medicinal uses (e.g., against pain, inflammation, nausea, and skin conditions), but the effects are largely anecdotal. A derivative, cuminaldehyde thiosemicarbazone1, has been studied for activity against the hepatitis C virus and colon cancer.
A final note: Cumin is the main flavor ingredient in taco sauce. The next time you go out for Taco Tuesday, you have cuminaldehyde to thank.
1. CAS Reg. No. 3811-20-9.
Chemical properties
clear colorless to yellow liquid
Chemical properties
Cuminaldehyde has a strong, pungent, cumin-like odor and similar taste.
Occurrence
Reported in a large number of essential oils, cumin, Acacia farnesiana, cinnamon, bitter orange, Mexican lime, Eucalyptus globulus, rue, boldus, Artemisia hausiliensis and others. Also reported in lemon and mandarin peel oil, cinnamon bark, anise, clove bud, cumin seed, turmeric, parsley, calabash nutmeg (Monodora myristica Dunal), angelica root, thyme, beef, brandy, grape and mastic gum fruit oil.
The Uses of Cuminaldehyde
Cuminaldehyde is a flavoring agent that is a liquid, colorless to yellow in appearance, with a strong pungent odor resembling cumin oil. It is insoluble in water and soluble in alcohol and ether. It is obtained from cumin oil. It is also termed p-, cumaldehyde, and cuminal.
The Uses of Cuminaldehyde
Cuminaldehyde has been used to study larvicidal and adulticidal toxicity of monoterpenes against Culex pipiens. It has been used in evaluation of chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of essential oil and various extracts of Eucalyptus gilii.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of benzaldehydes that is benzaldehyde substituted by an isopropyl group at position 4. It is a component of essential oils from Cumin and exhibits insecticidal activities.
Preparation
From p-isopropylbenzyl chloride and hexamethylenetetramine (Arctander, 1969).
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 10 ppm: spicy with green cumin and herbal nuances.
General Description
Cuminaldehyde is a constituent of cumin oil that exhibits strong antifungal and antibacterial activities.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cuminaldehyde increases the insulin secretion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. It suppresses melanin formation in cultured murine B16-F10 melanoma cells.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. A skin irritant. Combustible liquid. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ALDEHYDES.
Synthesis
Prepared synthetically by heating p-isopropyl benzoyl chloride with an aqueous or alcoholic hexamethylenetetraamine solution.
Purification Methods
A likely impurity is the benzoic acid. Check the IR for the presence of OH from CO2H, and the CO frequencies. If the acid is present, then dissolve the aldehyde in Et2O, wash it with 10% NaHCO3 until effervescence ceases, then with brine, dry over CaCl2, evaporate and distil the residual oil, preferably under vacuum. It is almost insoluble in H2O, but soluble in EtOH and Et2O. The thiosemicarbazone has m 147o after recrystallisation from aqueous EtOH, MeOH or *C6H6. [Crounse J Am Chem Soc 71 1263 1949, Bernstein et al. J Am Chem Soc 73 906 1951, Gensler & Berman J Am Chem Soc 80 4949 1958, Beilstein 7 H 318, 7 II 347, 7 III 1095, 7 IV 723.]
Properties of Cuminaldehyde
| Melting point: | 97 °C |
| Boiling point: | 235-236 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.977 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2341 | CUMINALDEHYDE |
| Flash point: | 200 °F |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble1mL/4ML, clear, colorless (70%) |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | colorless to yellow liquid |
| color | Clear colorless to yellow |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in dipropylene glycol. spicy cumin green herbal |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| JECFA Number | 868 |
| Merck | 14,2621 |
| BRN | 636547 |
| Dielectric constant | 11.0(15℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 122-03-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzaldehyde, 4-(1-methylethyl)-(122-03-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cuminaldehyde (122-03-2) |
Safety information for Cuminaldehyde
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Cuminaldehyde
Cuminaldehyde manufacturer
New Products
2-bromo 6-methyl pyridine 2,3 Diamino pyridine 2-amino-2,4-dimethylpentanamide 2-(2-CHLOROETHOXY)TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN METHYL PIPERAZINE-1-CARBOXYLATE DL-ALPHA-METHYLLEUCINE 4-bromo-1-cyclobutylpyrazole 2,3,6-Trimethoxy Pyridine 1-Difluoromethyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 2-Allyl-3-Hydroxy benzaldehyde 1-(4-Bromo-3-nitrophenyl)-1-propanone 1,5-Diiodopentane Trimethyl(phenylthio)silane 4-bromo methyl-2-cyano biphenyl 2-(2-Aminothiazol-4-yl) acetic acid Hcl 1,3-diphenylurea 3-Amino Acetophenone 3-oxopentanedioic acid 3-Nitro-5-acetyl iminodibenzyl Ammonium Chloride Ferrous Sulphate Activated Carbon Potassium Sulphate Sodium ChlorideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 122-03-2 98%View Details
122-03-2 98%View Details
122-03-2 -
 122-03-2 99%View Details
122-03-2 99%View Details
122-03-2 -
 Cuminaldehyde CAS 122-03-2View Details
Cuminaldehyde CAS 122-03-2View Details
122-03-2 -
 Cuminaldehyde CAS 122-03-2View Details
Cuminaldehyde CAS 122-03-2View Details
122-03-2 -
 Cuminaldehyde Liquid aroma, 50 L Drum, 122-03-2View Details
Cuminaldehyde Liquid aroma, 50 L Drum, 122-03-2View Details
122-03-2 -
 Cuminaldehyde (122-03-2) (C10H12O), Packaging Size: DrumView Details
Cuminaldehyde (122-03-2) (C10H12O), Packaging Size: DrumView Details
122-03-2 -
 Polycaprolactone diacrylate, Mn: 2000 > 98%View Details
Polycaprolactone diacrylate, Mn: 2000 > 98%View Details -
 Polycaprolactone(300)-PEG(3350)-Polycaprolactone(300) Dimethacrylate > 98%View Details
Polycaprolactone(300)-PEG(3350)-Polycaprolactone(300) Dimethacrylate > 98%View Details
