Capecitabine
Synonym(s):5′-Deoxy-5-fluoro-N-[(pentyloxy)carbonyl]cytidine;CAP;Capecitabine;Ro-9-1978
- CAS NO.:154361-50-9
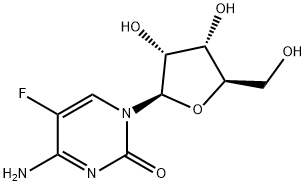
- Empirical Formula: C15H22FN3O6
- Molecular Weight: 359.35
- MDL number: MFCD00930626
- EINECS: 604-948-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-04-15 15:30:59
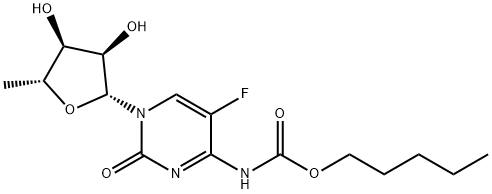
What is Capecitabine?
Absorption
The AUC of capecitabine and its metabolite 5’-DFCR increases proportionally over a dosage range of 500 mg/m2/day to 3,500 mg/m2/day (0.2 to 1.4 times the approved recommended dosage). The AUC of capecitabine’s metabolites 5’-DFUR and fluorouracil increased greater than proportional to the dose. The interpatient variability in the Cmax and AUC of fluorouracil was greater than 85%.
Following oral administration of capecitabine 1,255 mg/m2 orally twice daily (the recommended dosage when used as a single agent), the median Tmax of capecitabine and its metabolite fluorouracil was approximately 1.5 hours and 2 hours, respectively.
Toxicity
Adequate studies investigating the carcinogenic potential of capecitabine have not been conducted. Capecitabine was not mutagenic in vitro to bacteria (Ames test) or mammalian cells (Chinese hamster V79/HPRT gene mutation assay). Capecitabine was clastogenic in vitro to human peripheral blood lymphocytes but not clastogenic in vivo to mouse bone marrow (micronucleus test). Fluorouracil causes mutations in bacteria and yeast. Fluorouracil also causes chromosomal abnormalities in the mouse micronucleus test in vivo.
In studies of fertility and general reproductive performance in female mice, oral capecitabine doses of 760 mg/kg/day (about 2,300 mg/m2/day) disturbed estrus and consequently caused a decrease in fertility. In mice that became pregnant, no fetuses survived this dose. The disturbance in estrus was reversible. In males, this dose caused degenerative changes in the testes, including decreases in the number of spermatocytes and spermatids. In separate pharmacokinetic studies, this dose in mice produced 5’-DFUR AUC values about 0.7 times the corresponding values in patients administered the recommended daily dose.
Based on findings in animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], XELODA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Available human data on XELODA use in pregnant women is not sufficient to inform the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of capecitabine to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis caused embryo lethality and teratogenicity in mice and embryo lethality in monkeys at 0.2 and 0.6 times the exposure (AUC) in patients receiving the recommended dose of 1,250 mg/m2 twice daily, respectively. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Administer uridine triacetate within 96 hours for management of XELODA overdose. Although no clinical experience using dialysis as a treatment for XELODA overdose has been reported, dialysis may be of benefit in reducing circulating concentrations of 5’-DFUR, a low–molecular-weight metabolite of the parent compound.
Description
Capecitabine is a new oral fluoropyrimidine carbamate for patients with advanced neoplastic disease, approved as Xeloda for the treatment of refractory metastatic breast cancer after failure on Paclitaxel and an anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimen ; it is a prodrug of doxifluridine (5-fluorouracil ; 5-FU) activated by a cascade of 3 enzymes concentrated in human liver and cancer tissue, resulting in the selective release of 5-FU at the tumor site and offering a prolonged tumour exposure to 5-FU. Oral Capecitabine passes intact through the intestinal mucosa, is converted first by carboxylesterase to 5'-deoxy-5- fluorocytidine in the liver, then by cytidine deaminase to 5'-deoxy-5-fluorouridine in the liver and tumour tissues and finally by thymidine phosphorylase to 5-FU in tumors. Therefore, Xeloda is much safer and more effective than 5-FU (for example, in the HCT116 human colon cancer and the MX-1 breast cancer xenograft .models).
The Uses of Capecitabine
Capecitabine is an antineoplastic agent. Capecitabine is a prodrug of Doxifluridine (D556750).
Indications
Capecitabine holds indications for treating various cancer types. In colorectal cancer, it serves as a single agent or part of combination chemotherapy for adjuvant treatment in stage III colon cancer and for unresectable or metastatic cases. Additionally, it is utilized in combination chemotherapy perioperative treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer. For breast cancer, capecitabine is recommended for advanced or metastatic cases as a single agent if anthracycline- or taxane-containing chemotherapy is not suitable, or in combination with docetaxel after disease progression on prior anthracycline-containing chemotherapy. In gastric, esophageal, or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer, capecitabine is employed as part of combination chemotherapy for unresectable or metastatic cases or for HER2-overexpressing metastatic gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma in patients not previously treated for metastatic disease. Lastly, for pancreatic cancer, capecitabine is indicated as adjuvant treatment for adult pancreatic adenocarcinoma within a combination chemotherapy regimen.
Background
Capecitabine is an orally-administered chemotherapeutic agent used in the treatment of metastatic breast and colorectal cancers. Capecitabine is a prodrug, that is enzymatically converted to fluorouracil (antimetabolite) in the tumor, where it inhibits DNA synthesis and slows growth of tumor tissue.
What are the applications of Application
Capecitabine is An antiproliferative 5-fluorouracil releasing compound
Pharmacokinetics
Capecitabine, classified as a fluoropyrimidine carbamate within the antimetabolite group of antineoplastic agents, operates by impeding DNA synthesis, ultimately inducing cancer cell death. As an orally administered systemic prodrug, capecitabine remains relatively inactive until enzymatically converted into 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a process facilitated by enzymes found in elevated levels within many tumors. Unlike direct infusion of 5-FU, which can lead to gastrointestinal toxicity and diminished efficacy due to enzymatic conversion primarily occurring in the gastrointestinal tract, capecitabine offers a more targeted delivery approach. This is achieved through intact transport across the intestinal mucosa, allowing for preferential conversion to 5-FU within tumor cells. 5-FU, in turn, exerts its pharmacological effects by inhibiting thymidylate synthase, disrupting DNA and RNA synthesis, ultimately leading to protein synthesis disruption and apoptosis. Notably, population-based exposure-effect analyses have highlighted a correlation between the area under the curve (AUC) of 5-FU and the incidence of grade 3-4 hyperbilirubinemia, underscoring the importance of monitoring and adjusting dosages based on individual patient responses.
Metabolism
Capecitabine undergoes metabolism by carboxylesterase and is hydrolyzed to 5’-DFCR. 5’-DFCR is subsequently converted to 5’-DFUR by cytidine deaminase. 5’-DFUR is then hydrolyzed by thymidine phosphorylase (dThdPase) enzymes to the active metabolite
fluorouracil.
Fluorouracil is subsequently metabolized by dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase to 5-fluoro-5, 6-dihydro-fluorouracil (FUH2). The pyrimidine ring of FUH2 is cleaved by dihydropyrimidinase to yield 5-fluoro-ureido-propionic acid (FUPA). Finally, FUPA is cleaved by β-ureido-propionase to α-fluoro-β-alanine (FBAL).
Properties of Capecitabine
| Melting point: | 110-121°C |
| Density | 1.49±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 87℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble10mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
Safety information for Capecitabine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Capecitabine
| InChIKey | GAGWJHPBXLXJQN-UORFTKCHSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
AVD pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
SGMR PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
SNECOFRi PVT LTD
Vidgas science and technologies Pvt Ltd
Meenaakshi Molecules Pvt Ltd
New Products
3-N-BOC-(S)-AMINO BUTYRONITRILE 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 4-Acetyl-2-methylbenzoicacid Acetyl-meldrum's acid Ethyl-4-Pyrazole carboxylate 2,6 Di acetylpyridine 2,6-Pyridinedimethanol 5,7-Dichloro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine 5-Bromo-2-Methoxy-4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Iodopyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine 2-Chloro-3-Bromo-5-Amiopyridine METHYL-4-(BUTYRYLAMINO)3-METHYL-5-NITROBENZOATE TRANS-CYCLOBUTANE-1,2- DICARBOXYLIC ACID 5-Nitro indazole R-(-)-5-(2-AMINO-PROPYL)-2-METHOXY-BENZENESULFONAMIDE 1,3-cyclohexanedione 4-Aminophenaethylalchol (S)-(+)-4-BENZYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE 3-NITRO-5-ACETYL IMINODIBENZYL 4-FLUORO PHENYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 1.0 M IN THF 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL6-(2,4,4-TRI METHYL PHENYL)-2-PYRIDONE MONO ETHANOL AMINE(PIROCTONE OLAMINE)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 154361-50-9 98%View Details
154361-50-9 98%View Details
154361-50-9 -
 Capecitabine 98%View Details
Capecitabine 98%View Details
154361-50-9 -
 Capecitabine 97%View Details
Capecitabine 97%View Details -
 Capecitabine USP 99%View Details
Capecitabine USP 99%View Details -
 154361-50-9 Capecitabine 98%View Details
154361-50-9 Capecitabine 98%View Details
154361-50-9 -
 Capecitabine 154361-50-9 98%View Details
Capecitabine 154361-50-9 98%View Details
154361-50-9 -
 Capecitabine 154361-50-9 98%View Details
Capecitabine 154361-50-9 98%View Details
154361-50-9 -
 154361-50-9 99%View Details
154361-50-9 99%View Details
154361-50-9