Betaine
Synonym(s):(Carboxymethyl)trimethylammonium inner salt;Betaine;Oxyneurine;TMG;Trimethylglycine
- CAS NO.:107-43-7
- Empirical Formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular Weight: 117.15
- MDL number: MFCD00012123
- EINECS: 203-490-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-05-13 12:03:43
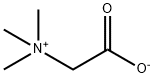
What is Betaine?
Absorption
Betaine is rapidly absorbed and distributed. In healthy volunteers (n=12) given 50 mg/kg of betaine, the Cmax, tmax and AUC0,∞ were 0.939 mmol/L, 0.90 h and 5.52 mmol?h/L, respectively. No significant changes in absorption kinetics were observed after repeated betaine administration (100 mg/kg/day for 5 days). The absolute bioavailability of betaine anhydrous has not been determined.
Toxicity
Toxicity information regarding betaine is not readily available. Patients experiencing an overdose are at an increased risk of severe adverse effects such as cerebral edema in patients with cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency. Symptomatic and supportive measures are recommended. In an acute toxicology study in rats, death frequently occurred at doses equal to or greater than 10,000 mg/kg. The effects of betaine on long-term carcinogenicity and fertility have not been evaluated. The following tests have not shown evidence of betaine genotoxicity: metaphase analysis of human lymphocytes, bacterial reverse mutation assay, and mouse micronucleus test.
Description
"Betaine" is the name of a class of zwitterionic compounds, but it is also commonly used to refer to glycine betaine, or trimethylglycine, pictured. Glycine betaine exists widely in nature; it was first isolated from the sugar beet Beta vulgaris, from which it takes its name. Betaine has many uses, including cosmetics, aircraft deicing, crop protection, fermentation, and animal and human nutrition.
The Uses of Betaine
betaine is a surfactant, humectant, and excellent skin conditioner. It is also used to build product viscosity and as a foam booster. It is found mostly in skin cleansers, shampoos, and bath products.
Background
Betaine is a methyl group donor that functions in the normal metabolic cycle of methionine. It is a naturally occurring choline derivative commonly ingested through diet, with a role in regulating cellular hydration and maintaining cell function. Homocystinuria is an inherited disorder that leads to the accumulation of homocysteine in plasma and urine. Currently, no treatments are available to correct the genetic causes of homocystinuria. However, in order to normalize homocysteine levels, patients can be treated with vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B12 (cobalamin), folate and specific diets. Betaine reduces plasma homocysteine levels in patients with homocystinuria. Although it is present in many food products, the levels found there are insufficient to treat this condition. The FDA and EMA have approved the product Cystadane (betaine anhydrous, oral solution) for the treatment of homocystinuria, and the EMA has approved the use of Amversio (betaine anhydrous, oral powder).
Indications
Betaine is indicated for the treatment of homocystinuria in pediatric and adult patients to decrease elevated homocysteine blood levels. Included within the category of homocystinuria are deficiencies or defects in cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS), 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), and cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl).
What are the applications of Application
Betaine is researched for its role in osmoregulation and methionine biosynthesis
Pharmacokinetics
Betaine decreases plasma homocysteine concentrations in homocystinuria cases caused by deficiencies or defects in cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS), 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), and cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl). The decrease of homocysteine is estimated to be 20-30% of pre-treatment levels. Betaine supplementation in patients with homocystinuria also improves metabolic abnormalities in cerebrospinal fluid. Reports have shown that depending on the type of homocystinuria, the therapeutic effectiveness of betaine alone may be limited, insufficient to decrease total homocysteine levels and prevent clinical symptoms. In patients with homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency, betaine should be used when serum total homocysteine levels remain high despite dietary therapy.
Patients taking betaine for several years do not show evidence of tolerance. Also, betaine concentrations are not correlated with homocysteine concentrations. In patients with MTHFR deficiency and cbl defects, betaine may increase methionine and S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) plasma levels. Patients with CBS deficiency without a dietary restriction of methionine may accumulate excessive amounts of methionine. Clinical data shows that in patients with CBS deficiency, increased plasma methionine levels were associated with cerebral edema.
Metabolism
Betaine is catabolized mainly in the mitochondria of liver and kidney cells. The transmethylation of betaine via betaine homocysteine methyl transferase (BHMT) leads to the formation of dimethylglycine.
Properties of Betaine
| Melting point: | 310 °C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 218.95°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: 0.1 g/mL, clear |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| color | colorless |
| Water Solubility | 160 g/100 mL |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Betaine
Computed Descriptors for Betaine
| InChIKey | KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
Jeevan Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
Unicorn Petroleum Industries Private Limited
HRV Global Life Sciences
Suvan LifeSciences (formerly Sansh Biotech Pvt Ltd)
New Products
3-N-BOC-(S)-AMINO BUTYRONITRILE 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 4-Acetyl-2-methylbenzoicacid Acetyl-meldrum's acid Ethyl-4-Pyrazole carboxylate 2,6 Di acetylpyridine 2,6-Pyridinedimethanol 5,7-Dichloro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine 5-Bromo-2-Methoxy-4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Iodopyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine 2-Chloro-3-Bromo-5-Amiopyridine METHYL-4-(BUTYRYLAMINO)3-METHYL-5-NITROBENZOATE TRANS-CYCLOBUTANE-1,2- DICARBOXYLIC ACID 5-Nitro indazole R-(-)-5-(2-AMINO-PROPYL)-2-METHOXY-BENZENESULFONAMIDE 1,3-cyclohexanedione 4-Aminophenaethylalchol 3-NITRO-5-ACETYL IMINODIBENZYL (S)-(+)-4-BENZYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE 4-FLUORO PHENYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 1.0 M IN THF 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL6-(2,4,4-TRI METHYL PHENYL)-2-PYRIDONE MONO ETHANOL AMINE(PIROCTONE OLAMINE)Related products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Betaine 99%View Details
Betaine 99%View Details -
 107-43-7 99%View Details
107-43-7 99%View Details
107-43-7 -
 Betaine 98%View Details
Betaine 98%View Details -
 Betaine 107-43-7 99%View Details
Betaine 107-43-7 99%View Details
107-43-7 -
 107-43-7 Betaine 98%View Details
107-43-7 Betaine 98%View Details
107-43-7 -
 68915-31-1 99%View Details
68915-31-1 99%View Details
68915-31-1 -
 Geraniol 99%View Details
Geraniol 99%View Details
106-24-1 -
 BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
8001-54-5