Adenosine
Synonym(s):9-β-D -Ribofuranosyladenine;Adenine riboside;Adenine-9-β-D -ribofuranoside
- CAS NO.:58-61-7
- Empirical Formula: C10H13N5O4
- Molecular Weight: 267.24
- MDL number: MFCD00005752
- EINECS: 200-389-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-05-18 08:51:57
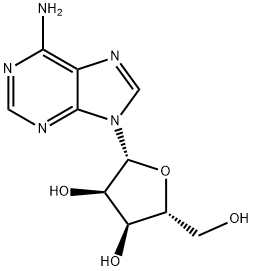
What is Adenosine?
Absorption
Data regarding the absorption of adenosine are not readily available.
Toxicity
Patients experiencing an overdose of adenosine may present with asystole, heart block, or cardiac ischemia; though the effects are generally short lived. Patients experiencing an overdose should be treated with symptomatic and supportive care, which may include a slow intravenous injection of theophylline.
The LD50 in mice is >20 g/kg subcutaneously, 500mg/kg intraperitoneally, and 39.6 μg/kg subcutaneously.
Description
Adenosine is a nucleoside composed of a molecule of adenine attached to a ribose sugar molecule (ribofuranose) moiety via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Adenosine works in the energy transfer-as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-as well as in signal transduction as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP. It shows neuromodulatory, cytoprotective, anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective actions.
Description
Adenosine is a nucleoside found widely in nature, and it is one of the components of the important energy-transfer coenzymes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and diphosphate (ADP). It was first isolated from yeast nucleic acid; several researchers reported its structure in the 1930s. More recently, M. Nedergaard and co-workers showed that adenosine released during acupuncture acts as a painkiller.
The Uses of Adenosine
adenosine is an amino acid. Studies indicate anti-wrinkle and skinsmoothing capacities. Although little is written about its direct skin benefit, adenosine plays an important role in biochemical processes. As adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP), it is involved in energy transfer, and as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in signal transduction.
What are the applications of Application
Adenosine is an apoptosis inducer and an Adenosine A Receptor activator
Indications
Adenosine is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 in myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in patients unable to adequately exercise. It is also indicated to convert sinus rhythm of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
Background
The structure of adenosine was first described in 1931, though the vasodilating effects were not described in literature until the 1940s. Adenosine is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 in myocardial perfusion scintigraphy, though it is rarely used in this indication, having largely been replaced by dipyridamole and [regadenson]. Adenosine is also indicated in the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia.
Adenosine was granted FDA approval on 30 October 1989.
Pharmacokinetics
Adenosine is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 in myocardial perfusion scintigraphy and also indicated for conversion of sinus rhythm of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Adenosine has a short duration of action as the half life is <10 seconds, and a wide therapeutic window. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of cardiovascular side effects, bronchoconstriction, seizures, and hypersensitivity.
Metabolism
Adenosine can be phosphorylated by adenosine kinase to form adenosine monophosphate. From there, it is phosphorylated again by adenylate kinase 1 to form adenosine diphosphate, and again by nucleoside diphosphate kinase A or B to form adenosine triphosphate.
Alternatively, adenosine can be deaminated by adenosine deaminase to form inosine. Iosine is phosphorylated by purine nucleoside phosphorylase to form hypoxanthine. Hypoxanthine undergoes oxidation by xanthine dehydrogenase twice to form the metabolites xanthine, followed by uric acid.
Properties of Adenosine
| Melting point: | 234-236 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 410.43°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3382 (rough estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, soluble in hot water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute mineral acids. |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water, ammonium hydroxide and dimethyl sulfoxide. Insoluble in ethanol. |
Safety information for Adenosine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Adenosine
| InChIKey | OIRDTQYFTABQOQ-KQYNXXCUSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Surajlok Chemicals Pvt Ltd (Neon Laboratories Ltd)
Bioaltus Laboratories Pvt Ltd
New Products
3-N-BOC-(S)-AMINO BUTYRONITRILE 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-Methyl-4-nitrobenzoic acid 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid 4-Acetyl-2-methylbenzoicacid Acetyl-meldrum's acid Ethyl-4-Pyrazole carboxylate 2,6 Di acetylpyridine 2,6-Pyridinedimethanol 5,7-Dichloro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine 5-Bromo-2-Methoxy-4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Iodopyridine 2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine 2-Chloro-3-Bromo-5-Amiopyridine METHYL-4-(BUTYRYLAMINO)3-METHYL-5-NITROBENZOATE TRANS-CYCLOBUTANE-1,2- DICARBOXYLIC ACID 5-Nitro indazole R-(-)-5-(2-AMINO-PROPYL)-2-METHOXY-BENZENESULFONAMIDE 1,3-cyclohexanedione 4-Aminophenaethylalchol 3-NITRO-5-ACETYL IMINODIBENZYL (S)-(+)-4-BENZYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE 4-FLUORO PHENYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 1.0 M IN THF 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL6-(2,4,4-TRI METHYL PHENYL)-2-PYRIDONE MONO ETHANOL AMINE(PIROCTONE OLAMINE)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 58-61-7 Adenosine,99% 99%View Details
58-61-7 Adenosine,99% 99%View Details
58-61-7 -
 58-61-7 98%View Details
58-61-7 98%View Details
58-61-7 -
 Adenosine 98%View Details
Adenosine 98%View Details
58-61-7 -
 68915-31-1 99%View Details
68915-31-1 99%View Details
68915-31-1 -
 Azadirachtin 11141-17-6 99%View Details
Azadirachtin 11141-17-6 99%View Details
11141-17-6 -
 Geraniol 99%View Details
Geraniol 99%View Details
106-24-1 -
 BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
8001-54-5 -
 Amrit Neem 11141-17-6 99%View Details
Amrit Neem 11141-17-6 99%View Details
11141-17-6