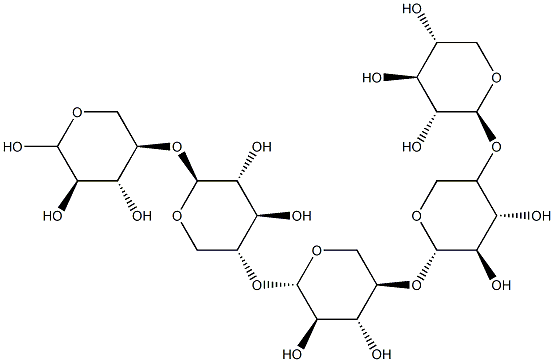
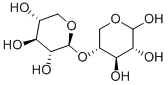
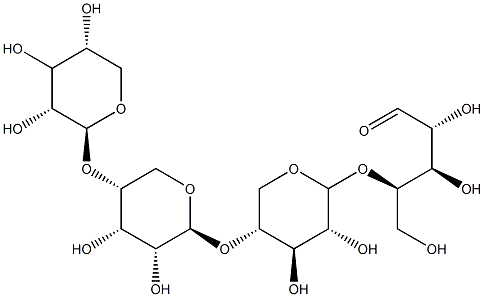
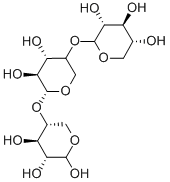
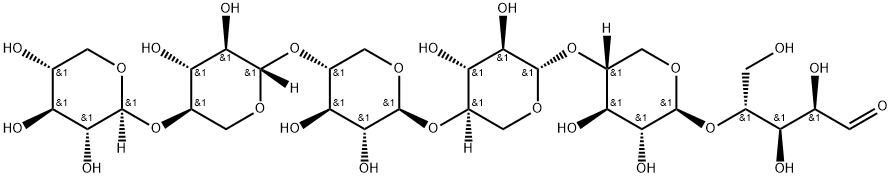
Xylohexaose
- CAS NO.:49694-21-5
- Empirical Formula: C30H50O25
- Molecular Weight: 810.71
- MDL number: MFCD28064299
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-07-02 08:55:00
What is Xylohexaose?
The Uses of Xylohexaose
Xylohexaose is a xylose oligomer that is of interest to many fields of study and is an intermediate reaction product of the hydrolysis of hemicelluloses.
Reactions
Most of the chemical and biochemical processes used for the de-polymerization of structural polymers of lignocellulosic biomass are environment unfriendly and costly. Here an efficient process based on xylanase, produced by Acinetobacter pittii MASK25 (MTCC 25132), hydrolysis of only physically treated rice straw and corn cob has been developed for the production of xylooligosaccharides. Bacterial strain isolated from soil was found to produce maximum xylanase at 30 °C and pH 7. While the optimum temperature and pH of xylanase were characterized as 40 °C and 5. Process was further improved by developing magnetic-xylanase CLEA. Crude xylanase and magnetic-xylanase CLEA could convert respectively more than 45percent and 60percent xylan of the powdered rice straw and corn cob into xylooligosaccharides. Interestingly, hydrolysis by both types of enzymatic forms was found to produce predominantly xylopentose and xylohexose. Hence, the process is environment friendly and the predominant production of xylopentose and xylohexose could find unique prebiotic applications.
Properties of Xylohexaose
| Melting point: | 236-237°C |
| Boiling point: | 1142.7±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | -70 º (c=1% in H2O) |
| Density | 1.77±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 12.40±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 49694-21-5 |
Safety information for Xylohexaose
Computed Descriptors for Xylohexaose
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(Hydroxymethyl)benzoate N-Boc-2-chloroethylamine 1-Bromo-2-methoxy-3-nitrobenzene N-Methyl-3-cyclopenten-1-amine 2-Bromo-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde 1H-indazole-5-carboxamideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 -
 1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 -
 (3-Benzyloxypropyl)triphenyl phosphonium 98%View Details
(3-Benzyloxypropyl)triphenyl phosphonium 98%View Details
54314-85-1 -
 4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride 1581266-79-6 98%View Details
4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride 1581266-79-6 98%View Details
1581266-79-6 -
 2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 -
 N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
5434-30-0 -
 124371-59-1 98%View Details
124371-59-1 98%View Details
124371-59-1 -
 53857-52-2 98%View Details
53857-52-2 98%View Details
53857-52-2