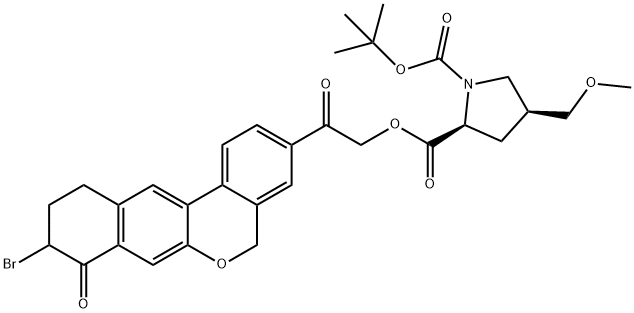
Velpatasvir
- CAS NO.:1377049-84-7
- Empirical Formula: C49H54N8O8
- Molecular Weight: 883
- MDL number: MFCD28411371
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
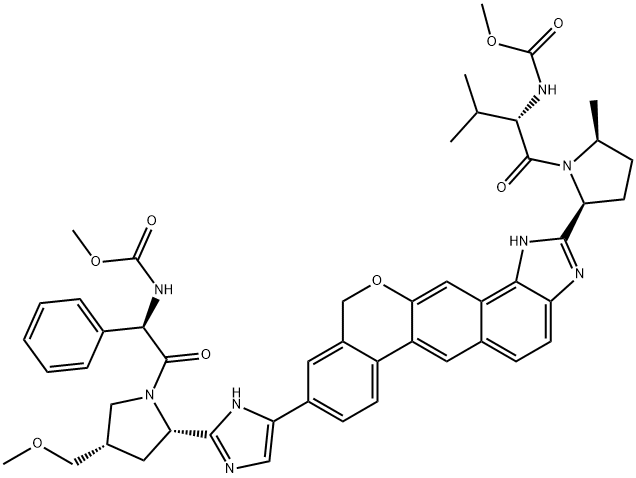
What is Velpatasvir?
Absorption
Oral bioavailability of 25-30% .
Toxicity
No indication of carcinogenicity or impairment of fertility/fetal viability .
Description
Velpatasvir (1377049-84-7) is an extremely potent pan-genotypic hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitor.1 It is a component of Epclusa? and Vosevi?, two clinically useful medications with 98% and 97%, respectively, cure rates for HCV.? It displayed EC50’s for GTs 1-4, 6a ranging from 6-16 pM, GT5a at 75 pM, and GT6e at 130 pM. Velpatasvir also displayed an excellent barrier to viral resistance. It has been shown in silico, that velpatasvir binds to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and may be a potential therapeutic.2
The Uses of Velpatasvir
Velpatasvir is a NS5A inhibitor in patients with hepatitis C (HCV) infection.
Indications
Velpatasvir is used in combination therapy with other antiviral medications to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infected patients with HCV genoptypes 1-6, and to treat HCV and HIV co-infected patients. Depending on the level of cirrhosis or decompensation, combination therapy can also include therapy with Ribavirin.
When used in combination with Sofosbuvir as the combination product Epclusa, Velpatasvir is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis, or in combination with Ribavirin if associated with decompensated cirrhosis .
Background
Velpatasvir is a Direct-Acting Antiviral (DAA) medication used as part of combination therapy to treat chronic Hepatitis C, an infectious liver disease caused by infection with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). HCV is a single-stranded RNA virus that is categorized into nine distinct genotypes, with genotype 1 being the most common in the United States, and affecting 72% of all chronic HCV patients . Velpatasvir acts as a defective substrate for NS5A (Non-Structural Protein 5A), a non-enzymatic viral protein that plays a key role in Hepatitis C Virus replication, assembly, and modulation of host immune responses . Treatment options for chronic Hepatitis C have advanced significantly since 2011, with the development of Direct Acting Antivirals (DAAs) such as velpatasvir. Notably, velpatasvir has a significantly higher barrier to resistance than the first generation NS5A inhibitors, such as Ledipasvir and Daclatasvir, making it a highly potent and reliable alternative for treatment of chronic Hepatitis C .
In a joint recommendation published in 2016, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) recommend Velpatasvir as first line therapy in combination with sofosbuvir for all six genotypes of Hepatitis C . Velpatasvir is currently only available within a fixed dose combination product as Epclusa with Sofosbuvir, another direct acting antiviral. Goals of therapy for Epclusa include the intent to cure, or achieve a sustained virologic response (SVR), after 12 weeks of daily therapy. SVR and eradication of HCV infection is associated with significant long-term health benefits including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality and risk of requiring a liver transplant .
Since June 2016, Velpatasvir has been available as a fixed dose combination product with Sofosbuvir, as the commercially available product Epclusa. Epclusa is the first combination HCV product indicated for the treatment of all genotypes of Hepatitis C with or without cirrhosis. It is also currently the most potent HCV antiviral medication on the market with a sustained virologic response (SVR) after 12 weeks of therapy of 93-99% depending on genotype and level of cirrhosis and a high barrier to resistance . Both Canadian and American guidelines list Epclusa as a first line recommendation for all genotypes of HCV .
Definition
ChEBI: A complex organic heteropentacyclic compound that is a hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A inhibitor used in combination with sofosbuvir (under the brand name Epclusa) for treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C of all six major genotypes.
Pharmacokinetics
Velpatasvir is a small molecule direct-acting antiviral used in the treatment of hepatitis C in combination with sofosbuvir. Velpatasvir prevents viral replication by inhibiting non-structural protein 5A (NS5A) .
At a dose 5 times the recommended dose, velpatasvir does not prolong QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent .
Metabolism
Some metabolism by CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP3A4 .
References
Link et al. (2019), Discovery of velpatasvir (GS-5816): A potent pan-genotypic HCV NS5A inhibitor in the single-tablet regimens Vosevi? and Epclusa?; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 29 2415 Kadioglu et al. (2020), Identification of novel compounds against three targets of SARS CoV-2 coronavirus by combined virtual screening and supervised machine learning; Comput. Biol. Med. 133 104359
Properties of Velpatasvir
| Melting point: | >170oC (dec.) |
| Density | 1.314±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (>25 mg/ml) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 10.75±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | Pale yellow |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
Safety information for Velpatasvir
Computed Descriptors for Velpatasvir
Velpatasvir manufacturer
BDR Pharmaceuticals International Pvt Ltd
Aspen Biopharma Labs Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 1377049-84-7 Velpatasvir 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 Velpatasvir 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 -
 1377049-84-7 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 -
 Velpatasvir 99%View Details
Velpatasvir 99%View Details
1377049-84-7 -
 Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7 98%View Details
Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 -
 1377049-84-7 Velpatasvir 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 Velpatasvir 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 -
 1377049-84-7 Velpatasvir 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 Velpatasvir 98%View Details
1377049-84-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1