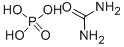
Urea nitrate
- CAS NO.:124-47-0
- Empirical Formula: CH5N3O4
- Molecular Weight: 123.07
- MDL number: MFCD00054386
- EINECS: 204-703-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
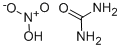
What is Urea nitrate?
Description
Urea nitrate, is a colorless crystal shipped with not less than 20% water by mass. It is a dangerous fire and explosion risk, and is slightly soluble in water. It decomposes at 305.6°F (152°C). The four-digit UN identification number is 1357. It is used in the manufacture of explosives and urethane.
Chemical properties
Colorless crystals. Decomposes at 152C. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol.
The Uses of Urea nitrate
As sensitizer for explosives; fertilizer; organic reagent; manufacture of urethane.
General Description
A crystalline compound arising from the neutralization of urea with nitric acid. Melting point 152°C. Slightly soluble in water. Soluble in alcohol. Primary hazard is blast of an instantaneous explosion, not flying projectiles or fragments.
Air & Water Reactions
Easily ignited. Burns very vigorously to generate toxic oxides of nitrogen. Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
UREA NITRATE is explosive when left in dry state. Wetting reduces possibility of explosion but may explode under prolonged exposure to heat or fire, even when wet. Urea nitrate reacts with strong oxidizer such as perclorates and hypochlorites. With hypochlorites Urea nitrate forms a compound nitrogen trichloride which explodes spontaneously in air (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 63:3530-32). Organic nitrates may explode when shocked, exposed to heat or flame or by spontaneous chemical reaction. Urea nitrate must be stored in a cool, ventilated place, away from acute fire hazards and easily oxidized materials. Also reacts violently with Al; BP; cyanides; esters; PN2H; P; NaCN; SnCl2; sodium hypophosphite; thiocyanates. Dangerous disaster hazard due to fire and explosion hazard. On decomposition, they emit toxic fumes. They are powerful oxidizing agents which may cause violent reaction with reducing materials. Nitrates should be protected carefully in storage. (SAX and Lewis, 1987) p.664. Decomposition is catalyzed by the presence of heavy metals such as lead or iron in trace amounts [Bretherick, 1995, pg. 201]. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Decomposed with explosive evolution of gas during the evaporation of an alkaline solution. [Bretherick, 1995, p. 201].
Health Hazard
Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases.
Fire Hazard
MAY EXPLODE AND THROW FRAGMENTS 1600 meters (1 MILE) OR MORE IF FIRE REACHES CARGO.
Safety Profile
A mild irritant. Flammable when exposed to heat or flame. The dry nitrate may explode when heated. The presence of heavy metals (e.g., lead, iron) catalyzes the thermal decomposition of urea nitrate. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from dilute HNO3 or EtOH (m 157-158o) and dry it in a vacuum over P2O5. [Beilstein 3 H 54, 3 I 25, 3 II 45, 3 III 105, 3 IV 94.]
Properties of Urea nitrate
| Melting point: | 152° with decompn |
| Boiling point: | 229.12°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.6900 |
| refractive index | 1.4164 (estimate) |
| Merck | 14,9869 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 124-47-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Urea mononitrate (124-47-0) |
Safety information for Urea nitrate
Computed Descriptors for Urea nitrate
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
