Tranexamic Acid
Synonym(s):AMCA;AMCHA;HAKU;TAMCHA;Tranexamic acid
- CAS NO.:1197-18-8
- Empirical Formula: C8H15NO2
- Molecular Weight: 157.21
- MDL number: MFCD00001466
- EINECS: 214-818-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:21
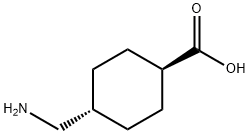
What is Tranexamic Acid?
Absorption
The bioavailability of tranexamic acid after oral administration in humans is approximately 30 to 50% of the ingested dose and is not affected by food intake. The Cmax and Tmax following multiple oral doses (1300 mg three times daily x 5 days) were 16.41 mcg/mL and 2.5 h, respectively.
Toxicity
Reported symptoms of tranexamic acid overdose include severe gastrointestinal symptoms, hypotension, thromboembolism, visual impairment, convulsions, mental status changes, and rash.
Description
Tranexamic acid is a derivative of aminomethylbenzoic acid, and a kind of antifibrinolytic drugs to stop bleeding. The hemostasis mechanism of tranexamic acid is similar to aminocaproic acid and aminomethylbenzoic acid, but the effect is stronger. The strength is 7 to 10 times of aminocaproic acid, 2 times of aminomethylbenzoic acid, but toxicity is similar.
The chemical structure of tranexamic acid is similar to lysine, competitive inhibition of plasmin original in fibrin adsorption, to prevent their activation, protection fiber protein not to degrade by plasmin and dissolve, eventually achieve hemostasis. Applicable in the treatment of acute or chronic, localized or systemic primary fiber fibrinolytic hyperthyroidism caused by bleeding, such as obstetric hemorrhage, renal hemorrhage, hemorrhage of hypertrophy of the prostate, hemophilia, pulmonary tuberculosis hemoptysis, stomach bleeding, after operation of liver, lung, spleen and other viscera hemorrhage; also can be used in surgery when abnormal bleeding etc..
Clinical tranexamic acid has effect significantly to insect bites disease, dermatitis and eczema, simple purpura, chronic urticaria, artificial sex urticaria, toxic eruption and eruption. And also has a certain effect on erythroderma, scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Erythema multiforme, shingles and alopecia areata. Treatment of hereditary angioedema effect is also good. In the treatment of Chloasma, general medicine is effective about 3 weeks, markedly effective 5 weeks, a course of 60 days. Given orally in doses of 0.25 ~ 0.5 g, a day 3 ~ 4 times. A few patients can nausea, fatigue, pruritus, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea side effects after withdrawal symptoms disappear.
Chemical properties
Tranexamic acid is a White or almost white, crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water and in glacial acetic acid and is very slightly soluble in ethanol and practically insoluble in ether.
Originator
Anvitoff,Knoll,W. Germany,1967
The Uses of Tranexamic Acid
Fibrinolysis, the cleavage of fibrin by plasmin, is a normal step in the dissolution of fibrin clots after wound repair. Tranexamic acid is an inhibitor of fibrinolysis that blocks the interaction of plasmin with fibrin (IC50 = 3.1 μM). It is a lysine mimetic that binds the lysine binding site in plasmin. Antifibrinolytic agents have value when fibrinolytic activity is abnormally high or when coagulation is impaired.
Indications
Taken orally, tranexamic acid is indicated for the treatment of hereditary angioedema, cyclic heavy menstrual bleeding in premenopausal females, and other instances of significant bleeding in the context of hyperfibrinolysis. Given intravenously, tranexamic acid is indicated for short-term use (2-8 days) in patients with hemophilia to prevent or reduce bleeding following tooth extraction.
Background
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic derivative of lysine used as an antifibrinolytic in the treatment and prevention of major bleeding.
It was first patented in 1957 and received its initial US approval in 1986.
What are the applications of Application
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic agent that inhibits plasmin-induced fibrinolysis by binding plasmin
Definition
ChEBI: Tranexamic acid is a monocarboxylic acid. It has a role as an antifibrinolytic drug and a hematologic agent. It is functionally related to a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid.
Indications
Various bleedings caused by acute or chronic, localized or systemic primary hyperfibrinolysis; secondary hyperfibrinolytic state caused by disseminated intravascular coagulation. Generally do not use this product before heparinization.
Trauma or surgical bleeding in tissue and organs with abundant plasminogen activators such as prostate, urethra, lung, brain, uterus, adrenal glands, and thyroid.
An antagonist of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA), streptokinase, and urokinase.
Fibrinolytic hemorrhage caused by artificial abortion, early placental detachment, stillbirth and amniotic fluid embolism; and increased menorrhagia caused by pathological intrauterine fibrinolysis.
Cerebral neuropathy mild bleeding, such as subarachnoid hemorrhage and intracranial aneurysm hemorrhage, the effect of Amstat in this condition is better than that of other anti-fibrinolytic agents. Special attention must be paid to the risk of cerebral edema or cerebral infarction.For severe patients with surgical indications, this product can only be used as an adjuvant drug.
For the treatment of hereditary angioneurotic edema, it can reduce the number and severity of episodes.
Used in patients with hemophilia for their active hemorrhage in combination with others drug.
Hemophilia patients with factor VIII or factor IX deficiency in their tooth extraction or oral surgery in case of operating bleeding.
Manufacturing Process
In an autoclave, 2 grams of a mixture of cis- and trans-4- aminomethylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, which is obtained by catalytic reduction of p-aminomethylbenzoic acid in the presence of platinum catalyst and contains 60% by weight of cis-isomer was reacted at 200°C, for 8 hours with 20 ml of ethyl alcohol in which 0.44 gram of sodium metal had been dissolved. After cooling, the reaction solution was concentrated under a reduced pressure to give a white residue. This residue was dissolved in 40 ml of water and passed through a column of a strongly acidic cation ion_x0002_exchanger resin (NH4+). The eluate was concentrated under reduced pressure to form a white mass. An adequate amount of acetone was added thereto and 1.95 grams of white powder was obtained. This powder was recrystallized from water-acetone to give 1.85 grams (yield, 92.5%) of white crystalline powder having a melting point of 380° to 390°C (decomposition). This product was identified as trans-4-aminomethylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid by means of infrared spectrum.
Therapeutic Function
Coagulant
General Description
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic agent and is commonly used for heavy menstrual bleeding.
Mechanism of action
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic lysine amino acid derivative, which diminishes the dissolution of hemostatic fibrin by plasmin. In the presence of tranexamic acid, the lysine receptor binding sites of plasmin for fibrin are occupied, preventing binding to fibrin monomers, thus preserving and stabilizing fibrin’s matrix structure. This agent has a longer half-life, is approximately ten times more potent, and is less toxic than aminocaproic acid, which possesses similar mechanisms of action.
Pharmacokinetics
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic that competitively inhibits the activation of plasminogen to plasmin. At much higher concentrations it behaves as a noncompetitive inhibitor of plasmin similar to aminocaproic acid, a similar antifibrinolytic which is 10-fold less potent. Tranexamic acid binds more strongly than aminocaproic acid to both the strong and weak receptor sites of the plasminogen molecule in a ratio corresponding to the difference in potency between the compounds.
In patients with hereditary angioedema, inhibition of the formation and activity of plasmin by tranexamic acid may prevent attacks of angioedema by decreasing plasmin-induced activation of the first complement protein (C1).
Clinical Use
Haemostatic agent
Side Effects
Tranexamic acid is mostly well-tolerated.
Common
nausea (upset stomach)
vomiting (throwing up)
diarrhea
headache
Occasional
dizziness
giddiness
vision changes
Rare
stroke
blood clots in undesired areas
deep vein thrombosis
Synthesis
Tranexamic acid, trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane carboxylic acid (24.4.5), is synthesized from 4-methylbenzonitrile. Oxidation of the methyl group gives the mononitrile of terephthalic acid 24.4.2. The cyano group in this compound is reduced by hydrogen using Raney nickel as a catalyst. The benzene ring of the resulting 4- aminomethylbenzoic acid (24.4.3) is reduced to a cyclohexane moiety by hydrogen and a platinum catalyst, which forms an isomeric mixture of 4-aminomethylcyclohexane carboxylic acids (24.4.4), and the desired trans-isomer 24.4.5 is isolated by crystallization of the mixture of its sodium salts.

Metabolism
Tranexamic acid metabolism is poorly characterized but does not appear to be a significant means of drug elimination. According to prescribing information, approximately 1% and 0.5% of an orally administered dose are excreted as a dicarboxylic acid and acetylated metabolite, respectively.
Metabolism
Tranexamic acid is excreted as unchanged drug mainly by urinary excretion via glomerular filtration.
Side Effects
Mild side effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and muscle pain. If get worse, connect your doctor.
Serious side effects: coughing up blood, fainting, chest/jaw/left arm pain, pain/swelling/warmth in the groin/calf, swelling/weakness/redness/pain in the arms/legs, signs of a stroke (such as weakness on one side of the body, trouble speaking, sudden vision changes, confusion), vision changes (such as color vision changes, decreased vision/blindness). If any of these very serious side effects occur, get medical help right away.
Precautions
Before using tranexamic acid, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: bleeding in the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage), history of blood clots (such as in the legs, lung, brain, eye), certain heart diseases (irregular heartbeat, heart valve problems), blood clotting problems, kidney problems (including blood in the urine), irregular menstrual bleeding of unknown cause.
References
Intravenous use of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty DOI:10.1007/s00402-014-2081-x
www.childrensmn.org
dermnetnz.org
Tranexamic acid for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage. DOI:10.1097/01.aoa.0000552886.12061.3c
Sittig's Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia
The Renal Drug Handbook
Synthesis of Essential Drugs (2006, Elsevier) - libgen.lc
Spectrophotometric and spectrofluorimetric methods for the determination of tranexamic acid in pharmaceutical formulation. DOI:10.1248/CPB.55.364
Determination of plasma tranexamic acid using cation-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. DOI:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)84573-9
[1] A Pilbrant, J Vessman, M Schannong. “Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of tranexamic acid.” European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 20 1 (1981): 65–72.
Pharmacokinetics
Tranexamic acid 1 g was given intravenously to three healthy volunteers. Plasma concentrations decayed in three monoexponential phases. Most elimination occurred during the first eight hours, giving an apparent elimination half-life of approximately two hours. Plasma clearance ranged between 110-116 ml/min. The urinary recovery of tranexamic acid exceeded 95% of the dose. The oral bioavailability of tranexamic acid, calculated from 24-hour urinary excretion after oral and intravenous administration, was 34% of the dose[1].
Properties of Tranexamic Acid
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 281.88°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0806 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 1.72hPa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.4186 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Freely soluble in water and in glacial acetic acid, practically insoluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| pka | pKa 4.3 (Uncertain);10.6 (Uncertain) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 1g/6ml |
| Merck | 14,9569 |
| BRN | 2207452 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1197-18-8 |
Safety information for Tranexamic Acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Tranexamic Acid
| InChIKey | GYDJEQRTZSCIOI-LJGSYFOKSA-N |
Tranexamic Acid manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

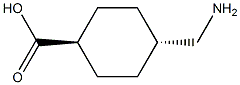

You may like
-
 1197-18-8 Tranexamic Acid 98%View Details
1197-18-8 Tranexamic Acid 98%View Details
1197-18-8 -
 Tranexamic Acid 99%View Details
Tranexamic Acid 99%View Details -
 Tranexamic acid 98%View Details
Tranexamic acid 98%View Details -
 1197-18-8 98%View Details
1197-18-8 98%View Details
1197-18-8 -
 Tranexamic acid 98% CAS 1197-18-8View Details
Tranexamic acid 98% CAS 1197-18-8View Details
1197-18-8 -
 trans-4-(Aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid CAS 1197-18-8View Details
trans-4-(Aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid CAS 1197-18-8View Details
1197-18-8 -
 Tranexamic acid impurity standard CAS 1197-18-8View Details
Tranexamic acid impurity standard CAS 1197-18-8View Details
1197-18-8 -
 Tranexamic acid CAS 1197-18-8View Details
Tranexamic acid CAS 1197-18-8View Details
1197-18-8
