TOMATINE
- CAS NO.:17406-45-0
- Empirical Formula: C50H83NO21
- Molecular Weight: 1034.19
- MDL number: MFCD00016888
- EINECS: 241-429-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-29 15:43:00
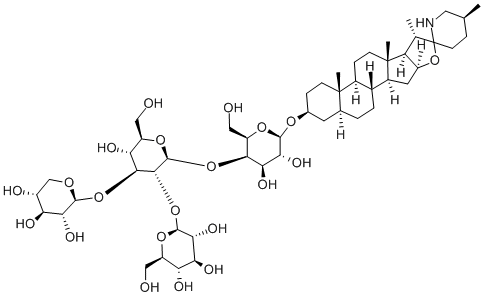
What is TOMATINE?
Description
This glycosidic alkaloid has been obtained from the dried leaves of Lycopersicum pimpinelli/olium (Syn. Solanum racemigerum) and also occurs in L. esculentum; L. hirsutum; L. peruvianum; L. peruvianum var. chutatum and L. putatum. The alkaloid forms colourless needles from MeOH and has a somewhat indefinite melting point about 270°C. It is laevorotatory with [α]20D - 30° (pyridine) and on hydrolysis with H2S04 yields tomatidine, I mole of galactose, 2 moles of glucose and 1 mole of xylose. The tetrasaccharide unit is known as lycotetraose. Partial hydrolysis with acid yields a series of products depending upon which, and how many, of the sugar residues are split off from the molecule. Those which have been isolated are: tomatidine lycotriose I (galactose-glucose-glucose); tomatidine lycotriose II (galactose-glucose-xylose); tomatidine lycobiose (galactose-glucose) and tomatidine-galactose.
Chemical properties
Faintly beige powder
The Uses of TOMATINE
Tomatine is used as an antiproliferatice agent used in the suppression of breast adenocarcinoma cells.
The Uses of TOMATINE
Precipitating agent for steroids.
What are the applications of Application
Tomatine is an antiproliferatve agent of breast adenocarcinoma cells
Definition
ChEBI: A steroid alkaloid that is tomatidine in which the hydroxy group at position 3 is linked to lycotetraose, a tetrasaccharide composed of two units of D-glucose, one unit of D-xylose, and one unit of D-galac ose.
Purification Methods
Tomatine is recrystallised from MeOH, EtOH, aqueous EtOH or dioxane/NH3. It is almost insoluble in pet ether, Et2O or H2O. [Reichstein Angew Chem 74 887 1962, Beilstein 27 III/IV 1954.]
References
Fontaine et al., Arch. Biochem., 18,467 (1948)
Kuhn, Low., Ber., 81, 552 (1948)
Kuhn, Low, Gauhe., ibid, 83,448 (1950)
Fontaine et al., Arch. Biochem., 27,461 (1950)
Fontaine et al., J. Amer. Chern. Soc., 73, 878 (1951)
Kuhn, Low, Trischmann., Angew. Chern., 68, 212 (1956)
Kuhn et al., Ber., 90, 203 (1957)
Properties of TOMATINE
| Melting point: | 300-305°C |
| Boiling point: | 806.69°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D20 -18° (c = 0.55 in pyridine) |
| Density | 1.48±0.1 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr) |
| refractive index | 1.5280 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated), Pyridine (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.77±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 14,9545 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 17406-45-0 |
Safety information for TOMATINE
Computed Descriptors for TOMATINE
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Tomatine from Tomato CAS 17406-45-0View Details
Tomatine from Tomato CAS 17406-45-0View Details
17406-45-0 -
 Tomatine CAS 17406-45-0View Details
Tomatine CAS 17406-45-0View Details
17406-45-0 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
