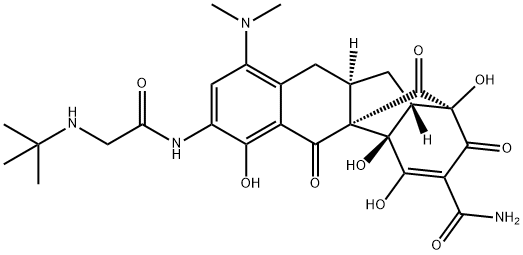
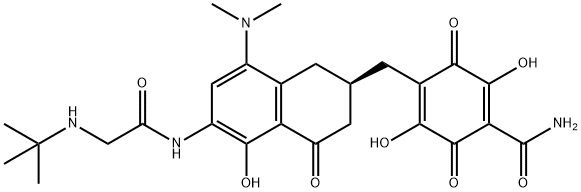
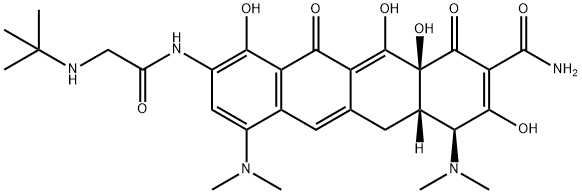
Tigecycline
Synonym(s):9- t-Butylglycylamido-minocycline;9-t-Butylglycylamido-minocycline;9-tert-Butylglycylamidominocycline;Tigecycline;Tigecycline - CAS 220620-09-7 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:220620-09-7
- Empirical Formula: C29H39N5O8
- Molecular Weight: 585.65
- MDL number: MFCD00935753
- EINECS: 685-736-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 14:33:46
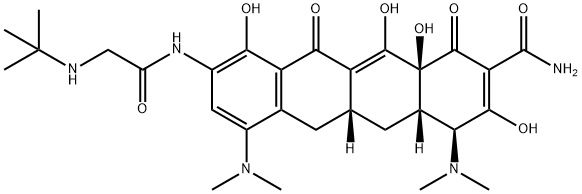
What is Tigecycline?
Toxicity
Since glycylcyclines are similar to tetracyclines, they share many of the same side effects and contraindications as tetracyclines. These side effects may include nausea/vomiting, headache, photosensitivity, discoloration of growing teeth, and fetal damage.
Description
The emergence of drug-resistant bacteria has diminished the clinical utility of the
tetracyclines. Research to circumvent the efflux and ribosomal protection mechanisms
of bacteria has led to the development of the glycylcyclines. Tigecycline is
the first glycylcycline antibiotic to launch for the parenteral treatment of
baterial infection, including complicated intra-abdominal and skin infections. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting protein translation in bacteria by binding
to the 30S ribosomal subunit and blocking entry of amino-acyl tRNA molecules
into the A site of the ribosome to effectively prevent incorporation of amino acid
residues into elongating peptide chains. Presumably, ribosomal protection proteins
are ineffective against tigecycline due to its higher affinity for ribosomal binding
compared to tetracyclines (approximately 16-fold). In addition, tigecycline may be
resistant to efflux mechanisms by either their inability to translocate it across the
cytoplasmic membrane due to steric complications or simply by their failure to
recognize the molecule.
Description
Tigecycline is a broad-spectrum glycylcycline antibiotic that binds to the bacterial 30S ribosome, blocking the entry of transfer RNA, which halts protein synthesis and inhibits bacterial growth. It is active against a panel of 1,924 European clinical bacterial isolates including S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. pneumoniae, E. faecalis, E. faecium, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, and P. mirabilis strains (MICs = <1-32 μg/ml). In vivo, tigecycline (6.25 mg/kg twice daily for 5 days) decreases levels of C. difficile cytotoxin activity and spore formation in cecum and colon in a mouse model of C. difficile infection. Formulations containing tigecycline have been used in the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections.
Chemical properties
Orange Solid
Originator
Wyeth (US)
The Uses of Tigecycline
Tigecycline is a semi-synthetic tetracycline analogue prepared by introducing a tert-butylaminoacetamide into a previously unexploited and unsubstituted region of an existing tetracycline. Like other tetracyclines, Tigecycline reversibly binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibits protein translation by preventing aminoacyl-tRNA from entering the ribosomal A site. The enhanced activity can be attributed to a stronger binding affinity, thus minimising the impact of existing resistance mechanisms.Tigecycline is considered to be the first of a new class of glycylcyclic antibiotics. It is used for the treatment of infections with drug-resistant bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Acinetobacter baumannii. Tigecycline is also known to have anticancer properties and is used as an antineoplastic agent.
Indications
For the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the following conditions: Complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only), Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and -resistant isolates), Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus anginosus grp. (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), Streptococcus pyogenes and Bacteroides fragilis. Complicated intra-abdominal infections caused by Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only), Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates only), Streptococcus anginosus grp. (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides vulgatus, Clostridium perfringens, and Peptostreptococcus micros.
Background
Tigecycline is a glycylcycline antibiotic developed and marketed by Wyeth under the brand name Tygacil. It was developed in response to the growing prevalence of antibiotic resistance in bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. It was granted fast-track approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on June 17, 2005.
What are the applications of Application
Tigecycline is a broad spectrum glycylcycline antibiotic
Definition
ChEBI: Tetracycline in which the hydroxy group at position 5 and the methyl group at position 6 are replaced by hydrogen, and with a dimethylamino substituent and an (N-tert-butylglycyl)amino substituent at positions 7 and 9, respe tively. A glycylcycline antibiotic, it has activity against a broad range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including tetracycline-resistant organisms. It is used for the intravenous treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections ca sed by susceptible organisms.
brand name
Tygacil
Antimicrobial activity
It is as potent as, or more potent than,
earlier tetracyclines and activity is retained against strains
expressing acquired tetracycline resistance determinants. It
displays better activity than tetracycline, doxycycline or
minocycline against Streptococcus spp. and against Enterococcus
faecalis and E. faecium. Among Gram-negative organisms it
displays improved activity against Citrobacter freundii,
Escherichia coli, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella pneumoniae,
Salmonella spp., Serratia marcescens and Shigella spp. The
spectrum includes rapidly growing mycobacteria. Ps. aeruginosa,
Pr. mirabilis, other Proteus spp. and some strains of
Corynebacterium jeikeium are resistant. Activity against strains
expressing acquired resistance to earlier tetracyclines is
attributed to failure of the MFS efflux pumps to recognize
tigecycline, and to a novel mechanism of ribosome binding
that permits tigecycline to overcome ribosomal protection
mechanisms.
Comparative susceptibility data for some atypical pathogens
are not available. However, in common with earlier
tetracyclines,
it is active against Chlamydophila and Mycoplasma
spp. and rapidly growing Mycobacteria spp. It is less active
than minocycline or tetracycline against U. urealyticum.
General Description
Tigecycline (Tygacil) is a first-in-class (a glycylcycline) intravenousantibiotic that was designed to circumvent manyimportant bacterial resistance mechanisms. It is not affectedby resistance mechanisms such as ribosomal protection, effluxpumps, target site modifications, β-lactamases, or DNAgyrase mutations. Tigecycline binds to the 30S ribosomalsubunit and blocks peptide synthesis. The glycylcyclinesbind to the ribosome with five times the affinity of commontetracyclines. Tigecycline also possesses a novel mechanismof action, interfering with the mechanism of ribosomal protectionproteins. Tigecycline, unlike common tetracyclines,is not expelled from the bacterial cell by efflux pumpingprocesses.
Tigecycline is recommended for the treatment of complicatedskin and skin structure infections caused by E. coli,E. faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates), S. aureus(methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant isolates),S. pyogenes, and B. fragilis among others. Tigecycline is alsoindicated for complicated intra-abdominal infections causedby strains of Clostridium, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, andBacteroides. To reduce the development of resistance to tigecycline,it is recommended that this antibiotic be used onlyfor those infections caused by proven susceptible bacteria.Glycylcyclines are structurally similar to tetracyclines,and appear to have similar adverse effects. These mayinclude photosensitivity, pancreatitis, and pseudotumorcerebri. Nausea and vomiting have been reported.
Pharmaceutical Applications
9-T-butylglycylamido-minocycline. A compound of the glycylcycline class available as a powder for intravenous infusion.
Pharmacokinetics
Tigecycline is the first clinically-available drug in a new class of antibiotics called the glycylcyclines. Glycylcyclines are a new class of antibiotics derived from tetracycline. These tetracycline analogues are specifically designed to overcome two common mechanisms of tetracycline resistance, namely resistance mediated by acquired efflux pumps and/or ribosomal protection. Glycylcycline antibiotics have a similar mechanism of action as tetracycline antibiotics. Both classes of antibiotics bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit to prevent the amino-acyl tRNA from binding to the A site of the ribosome. However, the glycylcyclines appear to bind more effectively than the tetracyclines.
Pharmacokinetics
Cmax 100 mg intravenous infusion (1 h): 0.85–1 mg/L
Plasma half-life: 37–67 h
Volume of distribution: 7–10 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: 68%
Distribution and excretion
It is widely distributed and is concentrated in the gallbladder,
colon and lung. The volume of distribution is dose related and
variable, but is generally greater than that of older tetracyclines.
CSF penetration is poor. Tigecycline is excreted in the
feces and urine predominantly as the unchanged molecule.
The elimination half-life is long (37–67 h). Tigecycline clearance
is decreased by 20% in patients with renal failure. No
dosage adjustments are apparently necessary for tigecycline
in patients with renal impairment.
Clinical Use
Complicated skin and skin structure infections
Complicated intra-abdominal infections
Community-acquired bacterial pneumonia
Recommended principally for the treatment of infections with
multiresistant organisms.
Side Effects
Side effects typical of the group, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and headache, occur. Occasional cases of pancreatitis, hypoproteinemia, antibiotic-associated colitis and thrombocytopenia have also been reported.
Synthesis
It does not require dosage adjustment in patients with impaired renal function and is conveniently dosed every 12 hours. Synthesis of tigecycline started with nitration of 138 with potassium nitrate and concentrated sulfuric acid to give 9-nitro derivative 139 in 93 % yield as disulfate salt, which was hydrogenated over Pd/C in 2-methoxyethanol/ 2N sulfuric acid at 40 psi to provide 9-aminominocycline (140). Finally, 9-aminominocycline (140) is acylated directly with N-tert-butylglycyl chloride in a 1:5 mixture of acetonitrile and N, N-dimethylpropyleneurea (DMPU) with anhydrous sodium carbonate to give tigecycline (XX).

in vitro
tigecycline exihibited good in vitro activities. the range of mic90s was 0.12-0.5 μg/ml for vancomycin-susceptible and -resistant strains of enterococcus faecalis and enterococcus faecium [2]. tigecyclinewas concentrated in cells and eliminated primarily via biliary excretion. diminished renal function didn’t significantly alter its systemic clearance. tigecycline didn’t interfere with common cytochrome p450 enzymes, making pharmacokinetic drug interactions uncommon [3].the tissue penetration of tigecycline was excellent and the compound showed equivalence to imipenem/cilastatin in intra-abdominal infection and to vancomycin plus aztreonam in skin and skin structure infection [4].
in vivo
in an intraperitoneal systemic murine infection model, tigecycline exihibited in vivo activities against gisa, methicillin-susceptible s. aureus and methicillin-resistant s. aureus strains [2]. tigecycline and daptomycin showed similar in vivo efficacies against infections caused by the mssa strain (strain gc 4543) with the ed50s of 0.12 and 0.24 mg/kg, respectively. the ed50s of tigecycline was 0.72 mg/kg [2].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anticoagulants: possibly enhanced anticoagulant
effect of coumarins.
Oestrogens: possibly reduced contraceptive effects of
oestrogens (risk probably small).
Metabolism
Tigecycline is not extensively metabolized. In vitro studies with tigecycline using human liver microsomes, liver slices, and hepatocytes led to the formation of only trace amounts of metabolites. A glucuronide, an N-acetyl metabolite, and a tigecycline epimer (each at no more than 10% of the administered dose) are the primary metabolites.
Metabolism
Tigecycline is not thought to be extensively metabolised,
although some trace metabolites have been identified
including a glucuronide, an N-acetyl metabolite, and a
tigecycline epimer. Tigecycline is primarily eliminated
(about 60
%) via biliary excretion of unchanged drug and
some metabolites.
References
1) Greer (2006)?Tigecycline (Tygacil): the first in the glycylcycline class of antibiotics; Proc. (Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent.)?19?155 2) Peterson (2008)?A review of tigecycline – the first glycylcycline; Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents?32 Suppl 4?S215 3) Skrtic?et al.?(2011)?Inhibition of mitochondrial translation as a therapeutic strategy for human acute myeloid leukemia; Cancer Cell?20?674 4) Jia?et al.?(2016)?Tigecyclin targets nonsmall cell lung cancer through inhibition of mitochondrial function; Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol.?30?297 5) Hu?et al.?(2016)?Antibiotic drug tigecycline inhibits melanoma progression and metastasis in a p21CIP1/Waf1-dependent manner; Oncotarget?7?3171 6) D’Andrea?et al.?(2016)?The mitochondrial translational machinery as a therapeutic target in Myc-driven lymphomas.; Oncotarget?7?72415 7) Chen?et al.?(2019)?Inhibition of mitochondrial translation selectively targets osteosarcoma; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 515 9
Properties of Tigecycline
| Melting point: | 164-166°C |
| Boiling point: | 890.9±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.45±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to at least 25 mg/ml). |
| form | Orange powder |
| pka | 4.50±1.00(Predicted) |
| color | Orange |
| Merck | 14,9432 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 1 month. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 220620-09-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Tigecycline
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Tigecycline
| InChIKey | FPZLLRFZJZRHSY-HJYUBDRYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(=O)[C@]2(O)[C@@]([H])(C[C@@]3([H])C(=C2O)C(=O)C2=C(C(N(C)C)=CC(NC(CNC(C)(C)C)=O)=C2O)C3)[C@H](N(C)C)C(O)=C1C(N)=O |
Tigecycline manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
Sumar biotech LLP
Kavya Pharma
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Tigecycline 97%View Details
Tigecycline 97%View Details -
 Tigecycline 99%View Details
Tigecycline 99%View Details -
 Tigecycline Powder For InjectionView Details
Tigecycline Powder For InjectionView Details
220620-09-7 -
 Tigecycline IP/USP/EP/BP CAS No.220620-09-7View Details
Tigecycline IP/USP/EP/BP CAS No.220620-09-7View Details
220620-09-7 -
 Industrial Grade Tigecycline USPView Details
Industrial Grade Tigecycline USPView Details
220620-09-7 -
 Tigecycline IP GradeView Details
Tigecycline IP GradeView Details
220620-09-7 -
 Tigecycline ApiView Details
Tigecycline ApiView Details
220620-09-7 -
 Tigecycline, Grade Standard: pharma, 220620-09-7View Details
Tigecycline, Grade Standard: pharma, 220620-09-7View Details
220620-09-7
