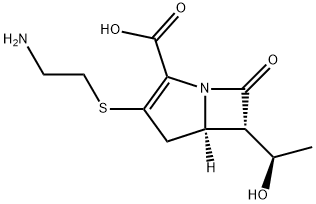
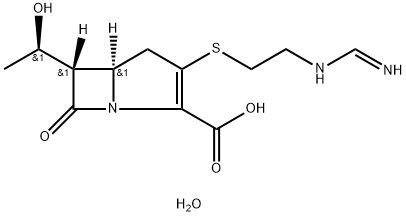
Thienamycin
- CAS NO.:59995-64-1
- Empirical Formula: C11H16N2O4S
- Molecular Weight: 272.32
- MDL number: MFCD00072032
- EINECS: 203-170-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-12 18:44:43
What is Thienamycin?
Description
Thienamycin, one of the most potent naturally-produced antibiotics known thus far, was discovered in Streptomyces cattleya in 1976. Thienamycin has excellent activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is resistant to bacterial β-lactamase enzymes.
The Uses of Thienamycin
Thienamycin is one of the most potent naturally produced antibiotics known thus far. It has excellent activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is resistant to bacterial β-lactamase enzymes.
What are the applications of Application
Thienamycin is a very potent antibiotic for cell culture and other research uses
Definition
ChEBI: Thienamycin is a member of carbapenems.
Biosynthesis
The formation of thienamycin is thought to occur through a different pathway from classic β-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins). Production of classic β-lactams in both fungi and bacteria occur through two steps: First, the condensation of L-cysteine, L-Valine, and L-α-amino adipic acid by ACV synthetase (ACVS, a nonribsomal peptide synthetase) and then cyclization of this formed tripeptide by isopenicillin N synthetase (IPNS).
Mechanism of action
In vitro, thienamycin employs a similar mode of action as penicillins through disrupting the cell wall synthesis (peptidoglycan biosynthesis) of various Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus,Staphylococcus epidermidis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa to name a few). In a study carried out by Spratt et al., they found that, although thienamycin binds to all of the penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) in Escherichia coli, it preferentially binds to PBP-1 and PBP-2, which are both associated with the elongation of the cell wall. Unlike pencillins, which are rendered ineffective through rapid hydrolysis by the β-lactamase enzyme present in some strains of bacteria, thienamycin remains antimicrobially active. Neu et al. found that thienamycin displayed high activity against bacteria that were resistant to other β-lactamase stable compounds (cephalosporins), highlighting the superiority of thienamycin as an antibiotic among β-lactams.
Clinical Use
Thienamycin itself is extremely unstable and decomposes in aqueous solution. Consequently, thienamycin is impractical for clinical treatment of bacterial infections. For this reason, stable derivatives of thienamycin were created for medicinal consumption. One such derivative, imipenem, was formulated in 1985. Imipenem, an N-formimidoyl derivative of thienamycin, is rapidly metabolized by the renal dihydropeptidase enzyme found in the human body. To prevent its rapid degradation, imipenem is normally co-administered with cilastatin, an inhibitor of this enzyme.
Properties of Thienamycin
| Boiling point: | 514.0±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D27 +82.7° (c = 1.0 in water) |
| Density | 1.50±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, -86°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| pka | 4.20±0.40(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-White to Dark Yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic, Temperature Sensitive, Very Unstable |
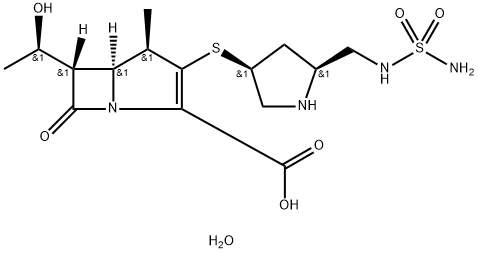
| InChI | InChI=1S/C11H16N2O4S/c1-5(14)8-6-4-7(18-3-2-12)9(11(16)17)13(6)10(8)15/h5-6,8,14H,2-4,12H2,1H3,(H,16,17)/t5-,6-,8-/m1/s1 |
Safety information for Thienamycin
Computed Descriptors for Thienamycin
| InChIKey | WKDDRNSBRWANNC-ATRFCDNQSA-N |
| SMILES | N12[C@@]([H])([C@@H]([C@H](O)C)C1=O)CC(SCCN)=C2C(O)=O |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 59995-64-1 Imipenem EP Impurity A 98%View Details
59995-64-1 Imipenem EP Impurity A 98%View Details
59995-64-1 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1