Tetrabenazine-d6
- CAS NO.:1392826-25-3
- Empirical Formula: C19H27NO3
- Molecular Weight: 317.43
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-22 22:33:46
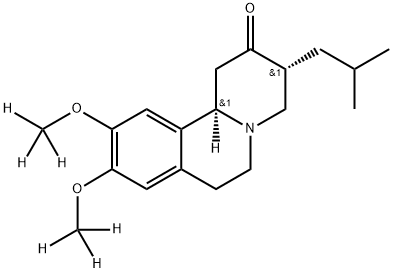
What is Tetrabenazine-d6?
Absorption
The extent of absorption is 80% with oral deutetrabenazine. As deutetrabenazine is extensively metabolized to its main active metabolites following administration, linear dose dependence of peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) and AUC was observed for the metabolites after single or multiple doses of deutetrabenazine (6 mg to 24 mg and 7.5 mg twice daily to 22.5 mg twice daily) . Cmax of deuterated α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ are reached within 3-4 hours post-dosing . Food may increase the Cmax of α-HTBZ or β-HTBZ by approximately 50%, but is unlikely to have an effect on the AUC .
Toxicity
Adverse reactions associated with overdosage include acute dystonia, oculogyric crisis, nausea and vomiting, sweating, sedation, hypotension, confusion, diarrhea, hallucinations, rubor, and tremor . In case of an overdose, general supportive and symptomatic measures are recommended while monitoring cardiac rhythm and vital signs. In managing overdosage, the possibility of multiple drug involvement should always be considered .
No carcinogenicity studies were performed with deutetrabenazine. In p53+/– transgenic mice, there were no detectable tumors following oral administration of deutetrabenazine at doses of 0, 5, 15, and 30 mg/kg/day for 26 weeks . Findings from in vitro assays and in vivo mice micronucleus assay suggest that deutetrabenazine and its metabolites are unlikely to be mutagenic . The effects of deutetrabenazine on fertility have not been evaluated. Oral administration of tetrabenazine had no effects on mating and reproductive systems of male and female rats .
Description
Tetrabenazine is a drug that was introduced in the 1950s as a tranquilizer. Since then it has been used to treat diseases such as Huntington’s chorea, Tourette syndrome, and hemiballismus.
This year, Israeli pharmaceutical giant Teva introduced an improved version of tetrabenazine: a?hexadeuterated form called deutetrabenazine. The six deuterium atoms are shown in green in the 3-D image.
The new drug takes advantage of the hydrogen–deuterium kinetic isotope effect, in which replacing hydrogen with deuterium slows the decomposition rate and allows it to remain in the body longer than the original.
In April, the US Food and Drug Administration approved deutetrabenazine for treating Huntington’s chorea. It is the first deuterated drug approved by the agency.
The Uses of Tetrabenazine-d6
Tetrabenazine-d6 is a dopamine depleting agent,it is used as an antidyskinetic,antipsychotic.
The Uses of Tetrabenazine-d6
Labeled Tetrabenazine, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Tetrabenazine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
The Uses of Tetrabenazine-d6
Labelled Tetrabenazine. Dopamine depleting agent. An antidyskinetic; antipsychotic.
Background
Deutetrabenazine is a novel, highly selective vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitor indicated for the management of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease. It is a hexahydro-dimethoxybenzoquinolizine derivative and a deuterated Tetrabenazine . The presence of deuterium in deutetrabenazine increases the half-lives of the active metabolite and prolongs their pharmacological activity by attenuating CYP2D6 metabolism of the compound . This allows less frequent dosing and a lower daily dose with improvement in tolerability . Decreased plasma fluctuations of deutetrabenazine due to attenuated metabolism may explain a lower incidence of adverse reactions associated with deutetrabenazine . Deutetrabenazine is a racemic mixture containing RR-Deutetrabenazine and SS-Deutetrabenazine .
Huntington's disease (HD) is a hereditary, progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor dysfunction, cognitive decline, and neuropsychiatric disturbances that interfere with daily functioning and significantly reduce the quality of life. The most prominent physical symptom of HD that may increase the risk of injury is chorea, which is an involuntary, sudden movement that can affect any muscle and flow randomly across body regions . Psychomotor symptoms of HD, such as chorea, are related to hyperactive dopaminergic neurotransmission . Deutetrabenazine depletes the levels of presynaptic dopamine by blocking VMAT2, which is responsible for the uptake of dopamine into synaptic vesicles in monoaminergic neurons and exocytotic release . As with other agents for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, deutetrabenazine is a drug to alleviate the motor symptoms of HD and is not proposed to halt the progression of the disease . In clinical trials of patients with HD, 12 weeks of treatment of deutetrabenazine resulted in overall improvement in mean total maximal chorea scores and motor signs than placebo . It was approved by FDA in April 2017 and is marketed under the trade name Austedo as oral tablets.
Indications
Deutetrabenazine is indicated in adults patients for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and for chorea associated with Huntington's disease.
What are the applications of Application
Tetrabenazine-d6 is a labeled tetrabenazine and dopamine depleting agent
Pharmacokinetics
In clinical trials, there was an evidence of clinical effectiveness of deutetrabenazine in improving the symptoms of involuntary movements in patient with tardive dyskinesia by reducing the mean Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) score . In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study in healthy male and female subjects, single dose administration of 24 mg deutetrabenazine results in an approximately 4.5 msec mean increase in QTc . Effects at higher exposures to deutetrabenazine or its metabolites have not been evaluated . Deutetrabenazine and its metabolites were shown to bind to melanin-containing tissues including eyes, skin and fur in pigmented rats. After a single oral dose of radiolabeled deutetrabenazine, radioactivity was still detected in eye and fur at 35 days following dosing .
Metabolism
Deutetrabenazine undergoes extensive hepatic biotransformation mediated by carbonyl reductase to form its major active metabolites, α-HTBZ and β--HTBZ. These metabolites may subsequently metabolized to form several minor metabolites, with major contribution of CYP2D6 and minor contributions of CYP1A2 and CYP3A4/5 .
Properties of Tetrabenazine-d6
| Melting point: | 126 - 127°C |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Tetrabenazine-d6
Computed Descriptors for Tetrabenazine-d6
Tetrabenazine-d6 manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidYou may like
-
 Deutetrabenazine 98%View Details
Deutetrabenazine 98%View Details -
 1392826-25-3 98%View Details
1392826-25-3 98%View Details
1392826-25-3 -
 Deutetrabenazine 1392826-25-3 98%View Details
Deutetrabenazine 1392826-25-3 98%View Details
1392826-25-3 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
