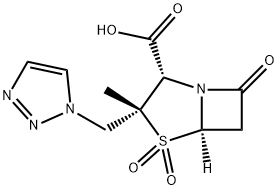
Tazobactam acid
Synonym(s):(2S,3S,5R)-3-methyl-7-oxo-3-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo-[3.2.0]heptanes-2-carboxylicacid-4,4-dioxide;[2S-(2α,3β,5α)]-3-Methyl-7-oxo-3-(1H,2,3-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptan-2-carbons?ure-4,4-dioxid;Tazobactam
- CAS NO.:89786-04-9
- Empirical Formula: C10H12N4O5S
- Molecular Weight: 300.29
- MDL number: MFCD00867002
- EINECS: 618-303-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-29 14:36:51
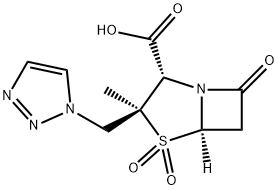
What is Tazobactam acid?
Absorption
Tazobactam is coadministered with piperacillin or ceftolozane, pharmacokinetic information will be provided for these combinations.
Piperacillin-tazobactam
Peak plasma concentrations occur immediately after the completion of intravenous infusion. Following several doses of piperacillin-tazobactam infusions every 6 hours, peak concentrations were similar to those that were measured after the initial dose.
Ceftolozane-piperacillin
AUC: 24.4-25 mcg?h/mL
Peak concentrations are reached on day 1 after the first dose and range from 18 to 18.4 mcg/mL.
Toxicity
Overdose
Post-marketing reports have been made of overdose cases with piperacillin/tazobactam. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are frequent manifestations of an overdose. Neuromuscular excitability or seizures may also occur with high intravenous doses or renal failure. There is no specific antidote. Provide supportive measures in case of an overdose. Anticonvulsive agents may be indicated when neuromuscular excitability or seizures occur. If anaphylaxis occurs, traditional measures should be taken to manage hypersensitivity (for example, adrenaline, antihistamines, corticosteroids, and oxygen/airway maintenance). Similar measures should be taken after a ceftolozane-tazobactam overdose. Hemodialysis can be used to remove the drug from the circulation .
A note on nephrotoxicity
Cases of life-threatening nephrotoxicity have been seen in critically ill patients receiving piperacillin-tazobactam. Alternative therapy and/or renal monitoring should be considered in critically ill patients.
Carcinogenesis/Mutagenesis
Tazobactam tested negative for genotoxic effects in the Ames assay, an after in vitro chromosomal aberration and point mutation assay in the Chinese hamster, an various other assays.
Use in pregnancy
Tazobactam has been found cross the placenta in rats. No data on human studies are available, however, rat studies have shown no teratogenetic effects at doses 6-14 times the equivalent maximum recommended human dose.
Use in lactation
There are no data on the presence of tazobactam in human breastmilk. No data are currently available on the effects of tazobactam on the infant, or how it affects milk production. Use clinical judgement and consider the maternal need for the drug and the benefits of breastfeeding the infant before administration during lactation. Small concentrations of piperacillin-tazobactam have been found in the breastmilk and can lead to hypersensitivity in a breastfeeding infant. In some cases, breastfeeding may have to be discontinued temporarily.
Description
Tazobactam often is coadministered with piperacillin because of tazobactam's ability to inhibit β-lactamases. T azobactam, like other β-lactamase inhibitors, has little or no antibacterial activity. This effect is analogous to that of clavulanic acid and sulbactam.
Chemical properties
White or off-white powder
Originator
CL-307579,China Pharm Chemical Co.,,China
The Uses of Tazobactam acid
b-lactamase inhibitor
The Uses of Tazobactam acid
Tazobactam is a β-Lactamase inhibitor, used with β-lactam antibiotics to enhance their effect.
Background
Tazobactam is an antibiotic of the beta-lactamase inhibitor class that prevents the breakdown of other antibiotics by beta-lactamase enzyme producing organisms. It is combined with Piperacillin and Ceftolozane for the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections.
Piperacillin-tazobactam was initially approved by the FDA in 1994, and ceftolozane-tazobactam was approved by the FDA in 2014, providing wider antibacterial coverage for gram-negative infections. In June 2019, ceftolozane-tazobactam was approved by the FDA for treating hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia, which are significant causes of morbidity and mortality in hospitalized patients.
Indications
Tazobactam is used in combination with piperacillin or ceftolozane to broaden the spectrum of piperacillin antibacterial action, treating susceptible infections. As with any other antibiotic, tazobactam should only be used for infections that are either proven or strongly suspected to be susceptible to the tazobactam containing drug.
Tazobactam-piperacillin
When combined with piperacillin, it is used to treat a variety of infections, including those caused by aerobic and facultative gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, in addition to gram-positive and gram-negative anaerobes. Some examples of infections treated with piperacillin-tazobactam include cellulitis, diabetic foot infections, appendicitis, and postpartum endometritis infections. Certain gram-negative bacilli infections with beta-lactamase producing organisms cannot be treated with piperacillin-tazobactam, due to a gene mutation conferring antibiotic resistance.
Tazobactam-ceftolozane
Tazobactam is used in combination with ceftolozane for the treatment of infections caused by designated susceptible microorganisms in adult and pediatric patients:
What are the applications of Application
Tazobactam, Free acid is a β-lactamase inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of penicillanic acids that is sulbactam in which one of the exocyclic methyl hydrogens is replaced by a 1,2,3-triazol-1-yl group; used (in the form of its sodium salt) in combination with ceftolozane sulfate for treatment of complicat d intra-abdominal infections and complicated urinary tract infections.
Manufacturing Process
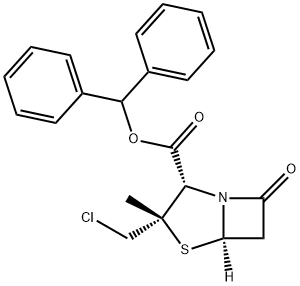
A known β-lactam type antibiotic (for example, benzhydryl 2-β-chloromethyl-
2-α-methylpenam-3-α-carboxylate) was used for synthesis of new penicillinic
derivatives.
A solution of 5.00 g of sodium azide in 53 ml of water was added to a solution
of benzhydryl 2-β-chloromethyl-2-α-methylpenam-3-α-carboxylate (5.13 g) in
dimethylformamide (155 ml). The mixture was stirred at room temperature
for 4 h. The resulting reaction mixture was poured into cooled water and the
mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate layer was washed
with water, dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated to provide 4.87 g
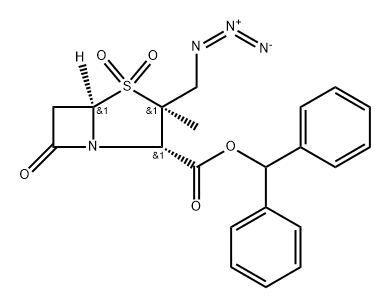
of the benzhydryl 2-β-azidomethyl-2-α-methylpenam-3-α-carboxylate as oil in
93% yield.
To a solution of benzhydryl 2-β-azidomethyl-2-α-methylpenam-3-α-
carboxylate (7.03 g) in a mixture of acetic acid (240 ml) and water (40 ml)
was added potassium permanganate (6.02 g) over a period of more than 1 h.
The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2.5 h. The resulting reaction
mixture was diluted with ice water. The precipitate was collected by filtration,
and washed with water. The resulting product was dissolved in ethyl acetate
and the solution was washed with an aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen
carbonate and dried over magnesium sulfate. Concentration gave 5.48 g of
the benzhydryl 2-β-azidomethyl-2-α-methylpenam-3-α-carboxylate-1,1-dioxide
in 72% yield.
A 200 mg quantity of benzhydryl 2-β-azidomethyl-2-α-methylpenam-3-α-
carboxylate-1,1-dioxide was reacted with 10 ml of vinyl acetate in a sealed reactor at 100° to 110°C for 30 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated at
reduced pressure. The residue was crystallized with cooled chloroform. The
white crystals of benzhydryl 2-α-methyl-2-β-(1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methylpenam-
3-α-carboxylate-1,1-dioxide have a melting point 206°-208°C, dec.
Hydrogenation was conducted in 10 ml of ethyl acetate and 10 ml of water at
room temperature for 30 min by using 45 mg of benzhydryl 2-α-methyl-2-β-
(1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methylpenam-3-α-carboxylate-1,1-dioxide, 15 mg of 10%
palladium charcoal and 16 mg of sodium hydrogen carbonate. The aqueous
layer was separated from the reaction mixture and washed once with ethyl
acetate. The aqueous solution was then purified with an MCl gel, CHP-20P
(product of Mitsubishi Kasei Co., Ltd., Japan). After freeze-drying, there was
obtained an amorphous product of sodium 2-α-methyl-2-β-(1,2,3-triazol-1-
yl)methylpenam-3-α-carboxylate-1,1-dioxide with a melting point 170°C, dec.
Therapeutic Function
Antibiotic
Antimicrobial activity
Tazobactam exhibits little useful antimicrobial activity, although weak activity against Acinetobacter spp. and Borrelia burgdorferi has been reported.
Mechanism of action
Tazobactam functions as an irreversible inhibitor by covalently binding to β-lactamases, and prevents the enzyme hydrolysis of ceftolozane, thereby enhancing its activity against resistant ESBL-producing pathogens, along with expanding coverage to include anaerobes (e.g., Bacteroides spp.)
Pharmacokinetics
Tazobactam inhibits the action of bacterial beta-lactamase producing organisms, which are normally resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics. This augments the effects of antibiotics which would otherwise not be effective in treating certain infections. These antibiotics contain a beta-lactam ring in their chemical structure, which is destroyed by beta-lactam resistant organisms. When combined with other antibiotics, a variety of infections, including serious and life-threatening infections may be treated.
Clinical Use
Tazobactam is a penicillanic acid sulfone that is similar instructure to sulbactam. It is a more potent β-lactamaseinhibitor than sulbactam and has a slightly broader spectrumof activity than clavulanic acid. It has very weak antibacterialactivity. Tazobactam is available in fixed-dose, injectablecombinations with piperacillin, a broad-spectrum penicillinconsisting of an 8:1 ratio of piperacillin sodium to tazobactamsodium by weight and marketed under the trade name Zosyn.The pharmacokinetics of the two drugs are very similar. Bothhave short half-lives (t1/2 ~1 hour), are minimally proteinbound, experience very little metabolism, and are excreted inactive forms in the urine in high concentrations.
Approved indications for the piperacillin–tazobactamcombination include the treatment of appendicitis, postpartumendometritis, and pelvic inflammatory disease caused byβ-lactamase–producing E. coli and Bacteroides spp., skin andskin structure infections caused by β-lactamase–producingS. aureus, and pneumonia caused by β-lactamase–producingstrains of H. influenzae.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Although veterinary experience is limited with piperacillin or piperacillin/ tazobactam, these drugs have expanded coverage against many bacteria and may be suitable for empiric use until culture and susceptibility data are available, or for surgical prophylaxis when gram-negative or mixed aerobic/anaerobic infections are concerns.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Reduced excretion of methotrexate - monitor
methotrexate levels during concomitant treatment.
Enhanced action of vecuronium and similar
neuromuscular blocking agents.
Metabolism
Tazobactam is mainly metabolized to M1, an inactive metabolite. Hydrolysis occurs on the beta-lactam ring to form M1 (the inactive metabolite).
Metabolism
Piperacillin is metabolised to a minor microbiologically
active desethyl metabolite. Tazobactam is metabolised
to a single metabolite that has been found to be
microbiologically inactive.
Piperacillin and tazobactam are eliminated via the
kidney by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion.
Piperacillin, tazobactam, and desethyl piperacillin are also
secreted into the bile.
Properties of Tazobactam acid
| Melting point: | 115-145℃ |
| Boiling point: | 77℃ |
| Density | 1.92±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| RTECS | XI0191400 |
| Flash point: | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly, Heated), Methanol (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated) |
| form | neat |
| pka | 2.33±0.40(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C10H12N4O5S/c1-10(5-13-3-2-11-12-13)8(9(16)17)14-6(15)4-7(14)20(10,18)19/h2-3,7-8H,4-5H2,1H3,(H,16,17)/t7-,8+,10+/m1/s1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 89786-04-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Tazobactam acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Tazobactam acid
| InChIKey | LPQZKKCYTLCDGQ-WEDXCCLWSA-N |
| SMILES | N12[C@@]([H])(CC1=O)S(=O)(=O)[C@@](C)(CN1C=CN=N1)[C@@H]2C(O)=O |
Tazobactam acid manufacturer
Nectar Lifesciences Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
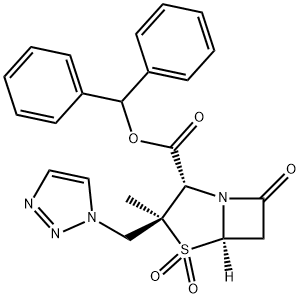
![BENZHYDRYL 6,6-DIHYDROPENICILLIC ACID 1-OXIDE[TAZOBACTAM INTERMEDIATE]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180713/GIF/87579-78-0.gif)

You may like
-
 89786-04-9 Tazobactam 98%View Details
89786-04-9 Tazobactam 98%View Details
89786-04-9 -
 Tazobactam >98% (HPLC) CAS 89786-04-9View Details
Tazobactam >98% (HPLC) CAS 89786-04-9View Details
89786-04-9 -
 Tazobactam CAS 89786-04-9View Details
Tazobactam CAS 89786-04-9View Details
89786-04-9 -
 Tazobactam CAS 89786-04-9View Details
Tazobactam CAS 89786-04-9View Details
89786-04-9 -
 Tazobactam CAS 89786-04-9View Details
Tazobactam CAS 89786-04-9View Details
89786-04-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1