Taurine
Synonym(s):2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid;Taurine
- CAS NO.:107-35-7
- Empirical Formula: C2H7NO3S
- Molecular Weight: 125.15
- MDL number: MFCD00008197
- EINECS: 203-483-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
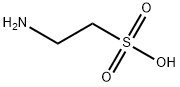
What is Taurine?
Absorption
Oral administration of taurine was studied and it reported dose-dependent values of AUC, Cmax and tmax wherein a dose of 1-30 mg/kg ranged from 89-3452 mcg min/L, 2-15.7 mcg min/ml and 15 min respectively. Further studies in healthy individuals gave an AUC, Cmax and tmax in the range of 116-284.5 mg h/L, 59-112.6 mg/L and 1-2.5 h.
Toxicity
The administration of taurine has been correlatefd to significant in the hypothalamus and the modification of neuroendocrine functions. Other than that, taurine administration in regular doses is reported by different articles and institutions to be safe.
Description
Taurine is a sulfur-containing amino acid with simple structure in animals. Its chemical name is 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid. Its molecular formula is C2H7NO3S and its molecular weight is 125.15. It is odorless and slightly sour. Its dilute solution is neutral and stable to heat. It combines with cholic acid in human and animal bile and exists in the form of binding; In brain, ovary, heart, liver, milk, pineal gland, pituitary, retina, adrenal gland and other tissues, it exists in free form, with a total amount of 12-18g, but does not participate in protein synthesis. Taurine is a conditionally essential amino acid for human body and plays an important role in the development of fetal and infant nervous system. Taurine can be widely used in medicine, food additives, fluorescent brighteners, organic synthesis and other fields. It can also be used as biochemical reagent, wetting agent, pH buffer and so on.
Description
Taurine, or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is the ingredient du jour in energy drinks (e.g., Red Bull). It was first isolated from ox bile (Taurus is Latin for ox). It is a major component of bile and found in animal muscle tissue. Scientists are pursuing its potential medicinal uses, which were discovered in part because cats cannot produce taurine and are subject to severe ailments when it is absent from their diet.
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder
Chemical properties
Taurine is a naturally occurring amino acid with a bitter taste and sharp flavor. It is a nonessential amino acid by definition because the body can synthesize it from methionine and cysteine.
Occurrence
Reported found in beef, black beans, chicken, chick peas, clams, cod, fish, lamb, milk, octopus, oysters, pistachios, pork, scallops, shrimp and other natural sources.
The Uses of Taurine
Taurine is an organic acid found in animal tissues and is a major constituent of bile. Taurine has many biological roles such as conjugation of bile acids, antioxidation, osmoregulation, membrane stabilization and modulation of calcium signaling. It is an amino acid nutritional supplement that is used to treat taurine-deficiency diseases such as dilated cardiomyopathy, a type of heart disease.
Background
Taurine, whose chemical name is 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is one of the most abundant amino acids in several organs. It plays important role in essential biological processes. This conditional amino acid can be either be manufactured by the body or obtained in the diet mainly by the consumption of fish and meat. The supplements containing taurine were FDA approved by 1984 and they are hypertonic injections composed by cristalline amino acids.
What are the applications of Application
Taurine is a compound that Inhibits lipid peroxidation
Indications
The use of diet supplements containing taurine is indicated for the nutritional support of infants and young pediatric patients requiring total parenteral nutrition via central or peripheral routes. The usage of diet supplements containing taurine prevents nitrogen and weight loss or to treat negative nitrogen balance in pediatric patients where the alimentary tract cannot be done through oral, gastrostomy or jejunostomy administration, there is impaired gastrointestinal absorption or protein requirements are substantially increased.
Definition
ChEBI: Taurine is an amino sulfonic acid that is the 2-amino derivative of ethanesulfonic acid. It is a naturally occurring amino acid derived from methionine and cysteine metabolism. An abundant component of fish- and meat-based foods, it has been used as an oral supplement in the treatment of disorders such as cystic fibrosis and hypertension. It has a role as a human metabolite, an antioxidant, a mouse metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite, a glycine receptor agonist, a nutrient and a radical scavenger. It is a conjugate acid of a 2-aminoethanesulfonate. It is a tautomer of a taurine zwitterion.
Biosynthesis
In addition to the intake of taurine directly from the diet, the animal body can also biosynthesis in the liver. The intermediate product of methionine and cysteine metabolism, cysteine, is decarboxylated to taurine by cysteine decarboxylase (CSAD), and then oxidized to taurine. CSAD is considered to be the rate limiting enzyme of taurine biosynthesis in mammals, and compared with other mammals, the activity of human CSAD is lower, which may be due to the low taurine synthesis ability in human body. Taurine can participate in the formation of taurocholic acid and hydroxyethyl sulfonic acid after decomposition in vivo. The amount of taurine required depends on cholic acid binding capacity and muscle content.
General Description
Taurine, which has chemistry similar to other amino acids, is important in several of the body's metabolic processes. Taurine is thought to have antioxidant properties. But little is known about the effects of long-term supplemental taurine use.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Taurine is an amino acid found in combination with bile acids [Hawley].
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: Taurine evolves highly toxic fumes when heated to decomposition, and may cause irritation on contact.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data are not available for Taurine, but Taurine is probably combustible.
Biological Activity
One of the most abundant free amino acids in the brain. A partial agonist at the inhibitory glycine receptor.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Non-selective endogenous agonist at glycine receptors. Conditionally essential sulfonated amino acid which modulates apoptosis in some cells; functions in many metabolic activities; a product of methionine and cysteine metabolism.
Pharmacokinetics
The diet supplements containing taurine are formulated as a well-tolerated nitrogen source for nutritional support. Administration of diet supplements regulates the level of plasma amino acid concentration, nitrogen balance, weight and serum protein concentration to reach normal values, thus improving the nutritional status.
Pharmacology
Taurine is an organic osmotic regulator. It not only participates in the regulation of cell volume, but also provides the basis for the formation of bile salts. It also plays an important role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Although taurine is a special amino acid not included in proteins, taurine is the most abundant amino acid in brain, retina and muscle tissue. Taurine is widely used, such as in the function of central nervous system, cell protection, cardiomyopathy, renal insufficiency, abnormal development of renal function and retinal nerve injury. Almost all eye tissues contain taurine. The quantitative analysis of rat eye tissue extract showed that taurine was the most abundant amino acid in retina, vitreous, lens, cornea, iris and ciliary body. Many studies have found that taurine is an active substance that regulates the normal physiological activities of the body. It has the functions of anti-inflammatory, analgesic, maintaining the osmotic pressure balance of the body, maintaining normal visual function, regulating the calcium balance of cells, reducing blood sugar, regulating nerve conduction, participating in endocrine activities, regulating lipid digestion and absorption, increasing the contractility of the heart, improving the immune capacity of the body, and enhancing the antioxidant capacity of cell membrane Protect a wide range of biological functions such as cardiomyocytes.
Safety Profile
Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx and NOx.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Taurine has proven beneficial in preventing retinal degeneration and the prevention and treatment of taurine-deficiency dilated cardiomyopathy in cats. Although modern commercial feline diets have added taurine, some cats still develop taurine-deficiency associated dilated cardiomyopathy. It may also be of benefit in taurine (±carnitine) deficient cardiomyopathy in American Cocker Spaniels and certain other breeds such as, Golden Retrievers, Labrador Retrievers, Newfoundlands, Dalmations, Portuguese Water Dogs, and English Bulldogs. Preliminary studies have shown evidence that it may be useful as adjunctive treatment for cardiac disease in animals even if taurine deficiency is not present. Because of its low toxicity, some have suggested it be tried for a multitude of conditions in humans and animals; unfortunately, little scientific evidence exists for these uses.
Metabolism
Taurine can be metabolized by diverse organisms to form different types of metabolites derived from the original form of taurine. In the human, the pathways that form the metabolism of taurine are divided in the formation of 5-glutamyl-taurine by the action of the enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase 6 or the formation of taurocholate by the action of the bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase.
storage
Store at RT
Properties of Taurine
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C |
| refractive index | 1.5130 (estimate) |
| FEMA | 3813 | TAURINE |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 1.5(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 4.5-6.0 (25℃, 0.5M in H2O) |
| Odor | bland |
| Water Solubility | 5-10 g/100 mL at 23.5 ºC |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.006 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.005 |
| Merck | 14,9074 |
| JECFA Number | 1435 |
| BRN | 1751215 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 107-35-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid(107-35-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Taurine (107-35-7) |
Safety information for Taurine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Taurine
| InChIKey | XOAAWQZATWQOTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
ShanPar Industries Pvt Ltd
Innovative Health Care (India) Pvt. Ltd.
Dr. Silviu Pharmachem Pvt., Ltd.
Humble Healthcare Limited
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Taurine Nutrient supplementView Details
Taurine Nutrient supplementView Details
107-35-7 -
 Taurine CAS 107-35-7View Details
Taurine CAS 107-35-7View Details
107-35-7 -
 Taurine CAS 107-35-7View Details
Taurine CAS 107-35-7View Details
107-35-7 -
 Taurine CAS 107-35-7View Details
Taurine CAS 107-35-7View Details
107-35-7 -
 2-Aminoethanesulfonic Acid CAS 107-35-7View Details
2-Aminoethanesulfonic Acid CAS 107-35-7View Details
107-35-7 -
 Taurine CASView Details
Taurine CASView Details -
 Taurine 99% CAS 107-35-7View Details
Taurine 99% CAS 107-35-7View Details
107-35-7 -
 Taurine CAS 107-35-7View Details
Taurine CAS 107-35-7View Details
107-35-7