Superoxide
- CAS NO.:11062-77-4
- Empirical Formula: O2*-
- Molecular Weight: 31.9988
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
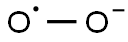
What is Superoxide?
Description
A product of the univalent reduction of O2 or the univalent oxidation of H2O2. The superoxide radical (O22 ) or its corresponding acid (perhydroxyl radical, HO2; pKa 5 4.8) is generated both enzymatically and nonenzymatically in biological systems. Superoxide can also be produced by cathodic reduction of O2 in an aprotic solvent, as well as by ultrasonication, pulse radiolysis, or photolysis of water. By virtue of a relatively negative dioxygen/superoxide couple (Eo0 5 20.31 V) superoxide is a stronger reductant than it is an oxidant (i.e., it readily reduces oxidized cytochrome C). Detection methods include optical spectroscopy, electron spin resonance, mass spectrometry, and detection of its presence based on its ability to reduce readily measurable oxidants such as cytochrome c or tetrazolium salts. Due to its reductive ability as well as the spontaneous disproportionation that proceeds with a rate constant of about 105 M21 sec21 (O22 1 O22 1 2H1-H2O2 1 O2), the steady-state concentrations of the oxyradicals are usually low at physiological conditions.
Definition
An inorganic compound containing the O2– ion.
Definition
superoxides: group of inorganiccompounds that contain the O2– ion.They are formed in significant quantitiesonly for sodium, potassium, rubidium,and caesium. They are verypowerful oxidizing agents and reactvigorously with water to give oxygengas and OH– ions. The superoxide ionhas an unpaired electron and is paramagneticand coloured (orange).
Properties of Superoxide
| Melting point: | 139-142 °C |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Superoxide (11062-77-4) |
Safety information for Superoxide
Computed Descriptors for Superoxide
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateYou may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1