Sulfathiazole
Synonym(s):N1-(2-Thiazolyl)sulfanilamide;2-Sulfanilamidothiazole;4-Amino-N-(2-thiazolyl)benzenesulfonamide;N1-2-Thiazolylsulfanilamid;Sulfathiazol
- CAS NO.:72-14-0
- Empirical Formula: C9H9N3O2S2
- Molecular Weight: 255.32
- MDL number: MFCD00005319
- EINECS: 200-771-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
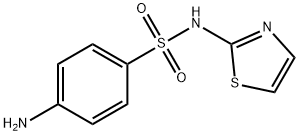
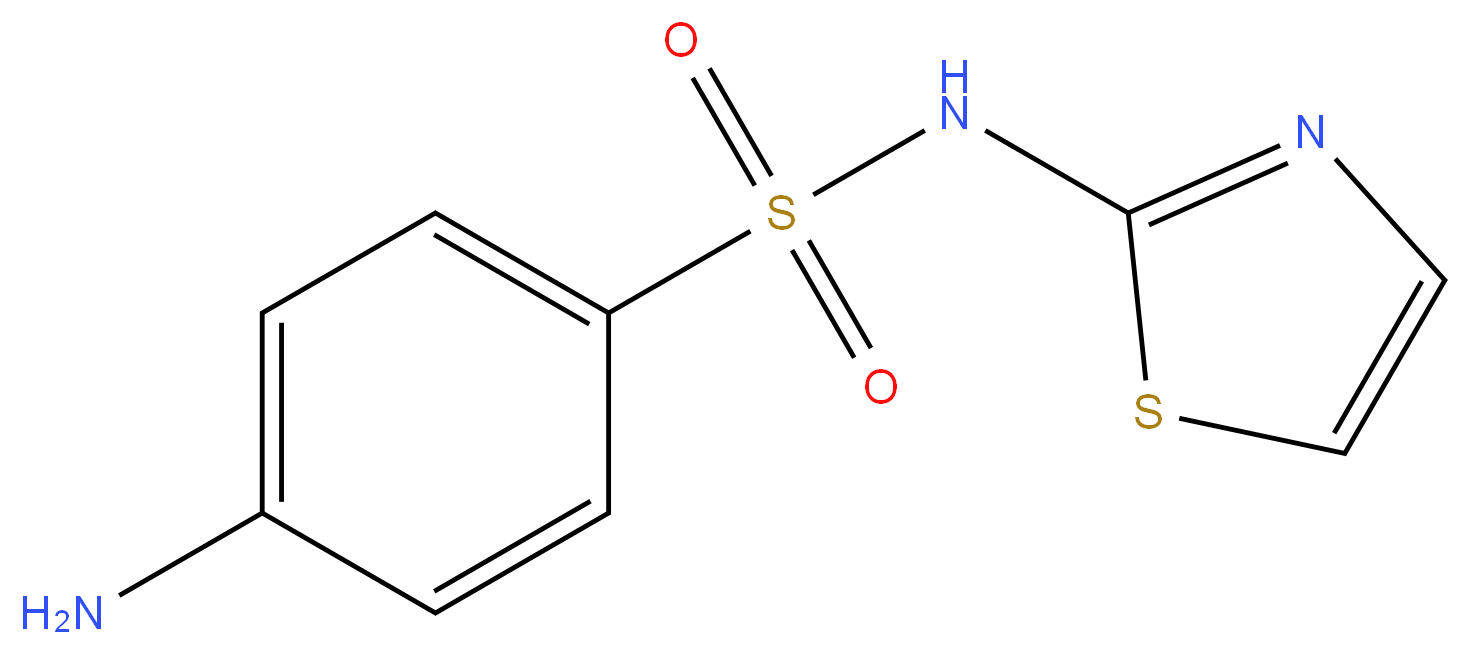
What is Sulfathiazole?
Toxicity
Acute oral toxicity (LD50): 4500 mg/kg [Mouse].
Chemical properties
white to cream powder
Originator
Tiazol,C. and C.
The Uses of Sulfathiazole
Sulfonamide antibacterial.
The Uses of Sulfathiazole
Antibacterial.This compound is a contaminant of emerging concern (CECs).
Indications
Sulfathiazole is effective against a wide range of gram positive and gram negative pathogenic microorganisms. Although no longer used in humans, it is used in cattle.
Background
Sulfathiazole is a short-acting sulfa drug. It used to be a common oral and topical antimicrobial until less toxic alternatives were discovered. It is still occasionally used, sometimes in combination with sulfabenzamide and sulfacetamide.
Except for those formulated for vaginal use, the FDA withdrew its approval for the use of all drug products containing sulfathiazole.
Definition
ChEBI: A 1,3-thiazole compound having a 4-aminobenzenesulfonamido group at the 2-position.
Manufacturing Process
116 parts 4-acetamidobenzolsufonyl chloride (prepared from acetanilide and
chlorosulfonic acid) was mixed with 100 parts 2-aminothiasole in 1000 parts
water by cooling and stirred for some hours. The bis-amide obtained was
filtered off and re-crystallized from 50% ethanol to give bis-(pacetylaminobenzolsulfo)-
2-aminothiazol with MP: 129°C.
10 parts above bis-amide was heated with 10% sodium hydroxide solution for
0.5 hour on water bath. On cooling and filtration the alkaline solution was
acidified with glacial acetic acid. The amide obtained was cleared by recrystallized
from water to give N1-2-thiazolylsulfanilamide; MP: 202°-203°C.
brand name
Argazol;Bucosol;Chemiovis;Coryza;Crionil;Csp 500;Csp-250;Edifeno;Femakzem;Formotablin antidiarreico;Gyne-sulf;Gyn-sulf;Neosutrin;Polvos wilfe;Pomada wilfe;Prothiazol;Septex cream no. 2;Streptacillin;Sulfa-orzon;Sulfazol;Sulfhatose;Sulfintestin;Sulfopyrol;Sulfour;Sulfzol;Sulnac;Sulphatriad;Tampovagan pss;Thiadyl;Thiuramide;Tiadyl;Trimeto;Trisulpha;Trysul;Tylasul;Ufa 902-duo;Vetoprim mi;Wintrazol.
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
World Health Organization (WHO)
Sulfathiazole, a sulfonamide anti-infective agent, was introduced more than 25 years ago for the treatment of bacterial infections. The importance of sulfonamides has subsequently decreased as a result of increasing bacterial resistance and their replacement by antibiotics which are generally more active and less toxic. The sulfonamides are known to cause serious adverse effects such as renal toxicity, sometimes fatal exfoliative dermatitis and erythema multiforma and dangerous adverse reactions affecting blood formation such as agranulocytosis and haemolytic or aplastic anaemia. Although preparations remain available, use of the drug has been discontinued in many countries.
General Description
White crystalline powder. Is dimorphous: form I is consists of prismatic rods and form II of six-sided plates and prisms. Insoluble in water and soluble in dil aqueous acid and aqueous base.
Air & Water Reactions
May be sensitive to heat, air and light during long-term storage . Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Sulfathiazole is an amino acid.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Sulfathiazole are not available, but Sulfathiazole is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
2-Sulfanilamidothiazole. A short-acting compound (half-life
c. 4 h) with relatively high activity. Protein binding is c. 75%.
Its use has declined because of a high incidence of side effects.
It is one of the constituents of triple sulfonamide mixtures, of
which local preparations are still available.
Two compounds, phthalylsulfathiazole (sulfathalidine) and
succinylsulfathiazole (sulfasuxidine) owe their activity to the
slow liberation of sulfathiazole in the bowel. They are poorly
soluble and very little is absorbed after oral administration.
They were formerly used in the treatment of intestinal infections
and in bowel preparation before surgery. They are available
in multi-ingredient preparations in some countries.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Sulfonamide antibiotic that blocks the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase.Mode of Action: Inhibits folic acid synthesis in prokaryotes.Anti-microbial Spectrum: Gram positive, Gram negative, ChlamydiaMode of Resistance: Alteration of dihydropteroate synthase or alternative pathway for folic acid synthesis.
Safety Profile
Human poison by unspecified route. Experimental poison by intraperitoneal route, Moderately toxic by intravenous, subcutaneous, and parenteral routes. Mildly toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects by unspecified route: conjunctiva irritation, tubule changes, and allergic skin dermatitis. Experimental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data, Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx.
Metabolism
Metabolism of sulfonamide drugs in animals includes conjugation at the N4-position (acetyl, sulfate, glucuronic acid, and glucose), conjugation at the N1-position (sulfate and glucuronic acid), removal of the p-amino group (formation of the desamino metabolite), ring hydroxylation, and conjugation of the ring hydroxylation products. Dietary nitrite enhances the production of the desamino metabolite of sulfathiazole. The intermediate leading to the desamino metabolite of sulfamethazine is weakly mutagenic in the Ames test (Nelson et al., 1987; Paulson et al., 1987).
Properties of Sulfathiazole
| Melting point: | 200-202 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 479.5±47.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.4629 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6560 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 0.5g/l |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 7.2(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble (<0.1 g/100 mL at 21 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,8943 |
| BRN | 226178 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 72-14-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Sulfathiazole(72-14-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sulfathiazole (72-14-0) |
Safety information for Sulfathiazole
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sulfathiazole
| InChIKey | JNMRHUJNCSQMMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Sulfathiazole manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 72-14-0 98%View Details
72-14-0 98%View Details
72-14-0 -
 72-14-0 Sulfathiazole 98%View Details
72-14-0 Sulfathiazole 98%View Details
72-14-0 -
 Sulfathiazole CAS 72-14-0View Details
Sulfathiazole CAS 72-14-0View Details
72-14-0 -
 Sulfathiazole 98% CAS 72-14-0View Details
Sulfathiazole 98% CAS 72-14-0View Details
72-14-0 -
 N1-2-Thiazolylsulfanilamid CAS 72-14-0View Details
N1-2-Thiazolylsulfanilamid CAS 72-14-0View Details
72-14-0 -
 Sulfathiazole CAS 72-14-0View Details
Sulfathiazole CAS 72-14-0View Details
72-14-0 -
 Sulfathiazole CAS 72-14-0View Details
Sulfathiazole CAS 72-14-0View Details
72-14-0 -
 Sulfathiazole CAS 72-14-0View Details
Sulfathiazole CAS 72-14-0View Details
72-14-0