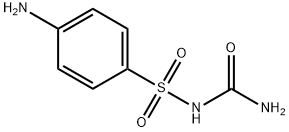
Sulfacarbamide
- CAS NO.:547-44-4
- Empirical Formula: C7H9N3O3S
- Molecular Weight: 215.23
- MDL number: MFCD00025437
- EINECS: 208-922-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-20 11:41:24
What is Sulfacarbamide?
Description
Sulfacarbamide is a blood sugar-lowering drug, also acting on the vegetative nervous system.
Chemical properties
White solid
The Uses of Sulfacarbamide
antibacterial
The Uses of Sulfacarbamide
Sulfacarbamide-d4 is the labeled analogue of Sulfacarbamide (S688945), an antibiotic which is rapidly absorbed in blister fluid.
Definition
ChEBI: Sulfacarbamide is a sulfonamide and a member of benzenes.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Sulfacarbamide, a sulfonamide anti-infective agent, was introduced in the 1940's for the treatment of bacterial infections. The importance of sulfonamides has subsequently decreased as a result of increasing bacterial resistance and their replacement by antibiotics which are generally more active and less toxic. The Sulfacarbamide are known to cause serious adverse effects such as renal toxicity, sometimes fatal exfoliative dermatitis and erythema multiforma and dangerous adverse reactions affecting blood formation such as agranulocytosis and haemolytic or aplastic anaemia. Sulfacarbamide still remains available in at least one country for the treatment of urinary infections.
Mechanism of action
Sulfonylureas bind to and inhibit the ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K) on the pancreatic beta cells. As a result, potassium efflux decreases, and the beta-cell membrane depolarizes. Membrane depolarization causes calcium channels to open, leading to calcium influx and increased intracellular calcium, which stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cells. Sulfonylureas cause insulin release regardless of blood glucose levels.
Properties of Sulfacarbamide
| Melting point: | 146-148° (slight dec) |
| Density | 1.4565 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6630 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2–8 °C |
| solubility | DMSO : ≥ 28 mg/mL (130.09 mM) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 1.78(H2O
t = 25
I = 0.05) (Uncertain);5.42(H2O
t = 25
I = 0.05) (Uncertain) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | 2.333g/L(20 ºC) |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C7H9N3O3S/c8-5-1-3-6(4-2-5)14(12,13)10-7(9)11/h1-4H,8H2,(H3,9,10,11) |
Safety information for Sulfacarbamide
Computed Descriptors for Sulfacarbamide
| InChIKey | WVAKABMNNSMCDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(S(NC(N)=O)(=O)=O)=CC=C(N)C=C1 |
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 1-SULFANILYLUREA CAS 547-44-4View Details
1-SULFANILYLUREA CAS 547-44-4View Details
547-44-4 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4