Soy bean phospholipid
- Molecular Weight: 0
- Update Date: 2024-06-07 16:36:03
What is Soy bean phospholipid?
The Uses of Soy bean phospholipid
Soy bean phospholipid is a source of choline and essential fatty acids and is widely used as a bioactive food additive. In addition, it is used as a wetting agent, solubiliser, emulsifier, liposome builder and technical aid in pharmaceutical, cosmetic or health nutritional products.
Preparation
Concentrated soybean phospholipids are products obtained by drying and dehydrating hydrated soybean crude oil foot. Industrial methods preparing concentrated soybean phospholipids include continuous and batch processings.
Biochem/physiol Actions
The mechanism of activity of Soy bean phospholipid is mainly based on their similarity to phospholipids found in biological membranes and blood lipoproteins. This similarity permits the incorporation of plant phospholipids into these structures and promotes the prevention of a number of pathological processes. Soya phospholipids have a wide range of biochemical and physical effects. Lecithin complexes are readily available sources of linoleic acid, choline and inositol. Lecithin also plays a significant role as an antioxidant booster. The health benefits of taking soy lecithin have been demonstrated and include lowering blood lipids, controlling blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels, stabilising membrane function, and supporting liver function.
Properties of Soy bean phospholipid
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
Safety information for Soy bean phospholipid
Computed Descriptors for Soy bean phospholipid
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



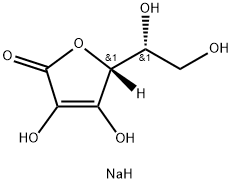
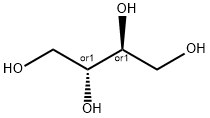



You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4