Sorafenib
- CAS NO.:284461-73-0
- Empirical Formula: C21H16ClF3N4O3
- Molecular Weight: 464.82
- MDL number: MFCD06411450
- EINECS: 608-209-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
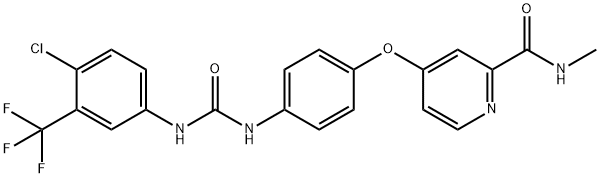
What is Sorafenib?
Absorption
The administration of multiple doses for seven days resulted in a 2.5- to 7-fold accumulation compared to a single dose. Steady-state concentrations were achieved within seven days, with a peak-to-trough ratio of mean concentrations of less than 2.
The mean relative bioavailability was 38–49% following the administration of oral sorafenib tablets. A high-fat meal reduced bioavailability by 29%.
Toxicity
The oral lowest published toxic dose (Toxic Dose Low, TDLo) is 2.84 mg/kg/21D (intermittent). The oral LD50 of sorafenib tosylate in rats is >2000 mg/kg.
The adverse reactions observed at 800 mg sorafenib twice daily (twice the recommended dose) were primarily diarrhea and dermatologic. No information is available on symptoms of acute overdose in animals because of the saturation of absorption in oral acute toxicity studies conducted in animals. The prescribing information recommends the discontinuation of sorafenib treatment and initiation of supportive care in cases of suspected overdose.
Description
Sorafenib is a small molecular inhibitor of several kinases involved in tumor angiogenesis and proliferation, including, but not limited to, Raf (IC50=12nM for Raf-1), VEGFR (IC50=90nM for VEGFR-2 and IC50=12nM for VEGFR-3), and platelet derived growth factor receptor (IC50=57nM for PDGFR-b). Specifically, sorafenib blocks tumor progression by inhibiting cellular proliferation that is dependent on activation of the MAPK pathway (Raf) and/or inhibiting tumor angiogenesis through VEGFR and/or PDGFR. While it may be effective in the treatment of a variety of tumors, the first approvable indication is for renal cell carcinoma. Overall, the drug appears to be well tolerated by the majority of patients at the 400 mg b.i.d. continuous dosing. As an inhibitor of multiple kinases vital for tumor progression, sorafenib may possess wide-spectrum antitumor properties and may emerge as an effective weapon against a variety of solid tumors.
Chemical properties
Light Yellow Solid
Originator
Bayer/Onyx (Germany)
Characteristics
Class: receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: RCC, HCC, thyroid cancer
Elimination half-life = 25–48 h
Protein binding = 99.7%
Characteristics
The complex of sorafenib with a nonphosphorylated VEGFR2 construct comprising the catalytic and juxtamembrane (JM) domain shows the activation loop adopts a DFG-out position. The net effect of sorafenib’s interactions with the kinase is to stabilize the DFG motif in an inactive conformation. The lipophilic trifluoromethyl phenyl ring at the opposite end of the molecule inserts into a hydrophobic pocket formed between the -C and -E helices and amino-terminal regions of the DFG motif and catalytic loop. The urea functionality forms two crucial hydrogen bonds, one with the backbone aspartate of the DFG loop and the other with the glutamate side chain of the -C helix. In the auto-inhibited state, the DFG-out segment, particularly Phe1047, blocks ATP-binding. When the JM rearranges out of the regulatory domain pocket (RDP), then the DFG is unlocked and able to switch to the open activated state. Autophosphorylation, which activates the kinase presumably through stabilization of an active conformation, was shown to occur on the JM and then the DFG-containing activation loop sequentially. Sorafenib fills the binding channel, making an important H-bond to Asp1046, two H-bonds to the side chain carboxylate oxygen of Glu885, and two H-bonds to Cys919. The selectivity of sorafenib derives from the formation of these four hydrogen bonds and attractive van der Waals (dispersion) interactions.
The Uses of Sorafenib
A potent RAF kinase inhibitor. Antineoplastic
The Uses of Sorafenib
Multiple kinase inhibitor targeting both RAF kinase and receptor tyrosine kinases that promote angiogensis. Antineoplastic.
The Uses of Sorafenib
Sorafenib Tosylate (Bay 43-9006, Nexavar) is a small molecular inhibitor of VEGFR, PDGFR, c-Raf and B-Raf with IC50s of 18 nM, 10 nM, 3 nM and 15 nM, respectively.
Background
Sorafenib is a bi-aryl urea and an oral multikinase inhibitor. It targets cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors and downstream intracellular kinases that are implicated in tumour cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. First approved by the FDA and European Commission in 2007 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, sorafenib is also indicated to treat renal carcinoma and differentiated thyroid carcinoma.
Indications
Sorafenib is indicated for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma and advanced renal cell carcinoma.
In the US, it is also indicated for the treatment of patients with locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, differentiated thyroid carcinoma that is refractory to radioactive iodine treatment.
Indications
Sorafenib (Nexavar(R), Bayer) was the first approved inhibitor targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family kinases, which include VEGFR1, VEGR2, and VEGFR3. Sorafenib was originally approved for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in 2005, hepatocellular carcinoma in 2007, and locally recurrent or metastatic thyroid carcinoma refractory to radioactive iodine treatment in 2013. Six other approved inhibitors with VEGFRs as the main targets are sunitinib (Sutent(R), Pfizer) for RCC, soft tissue sarcoma, thyroid cancer,metastatic pancreatic tumors, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, and several other types of carcinomas; pazopanib (Votrient(R), GlaxoSmithKline) for RCC, soft tissue sarcoma, and thyroid cancer; axitinib (Inlyta(R), Pfizer) for RCC,thyroid cancer, and aplastic anemia, as well as T315I-mutant Bcr–Abl1-driven leukemia; regorafenib (Stivarga(R), Bayer) for gastrointestinal stromal tumors and colorectal cancer; nintedanib (Ofev(R), Boehringer Ingelheim) for the non-oncological indication of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; and lenvatinib (Lenvima(R), Eisai Inc.) for RCC and different types of thyroid cancers. Sunitinib, pazopanib, and lenvatinib bind to the “DFG-in”conformation of VEGFRs, while axitinib, regorafenib, and nintedanib bind to inactive VEGFRs adopting the “DFG-out”conformation.
Definition
ChEBI: Sorafenib is a member of the class of phenylureas that is urea in which one of the nitrogens is substituted by a 4-chloro-3-trifluorophenyl group while the other is substituted by a phenyl group which, in turn, is substituted at the para position by a [2-(methylcarbamoyl)pyridin-4-yl]oxy group. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, an EC 2.7.11.1 (non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase) inhibitor, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, an angiogenesis inhibitor, an anticoronaviral agent and a ferroptosis inducer. It is a pyridinecarboxamide, a member of monochlorobenzenes, an aromatic ether, a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes and a member of phenylureas.
brand name
Nexavar (Bayer HealthCare); Xarelto (Bayer HealthCare).
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmacokinetics
Sorafenib decreases tumour cell proliferation in vitro. It attenuated tumour growth of human tumour xenografts in immunocompromised mice, reduced tumour angiogenesis, and increased tumour apoptosis in models of hepatocellular carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Some studies suggest that sorafenib induces apoptosis in several tumour cell lines, although this effect is inconsistent across cell lines.
Clinical Use
Protein kinase inhibitor:
Treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma
Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
Treatment of thyroid cancer
Synthesis
An improved, four-step synthesis in 63% overall yield
was published recently and is illustrated in the scheme.
Picolinic acid (127) was heated with Vilsmeier reagent for
16 hr to give 128 in 89% yield as an off-white solid. The
acid chloride 128 was treated with methylamine in methanol
at low temperature to give amide 129 in 88% yield as paleyellow
crystals after its crystallization from ethyl acetate.
4-Aminophenol anion was generated under a basic condition
and compound 129 was added to the anion solution to give
corresponding addition compound 131 in 87% yield. For an
unknown reason, potassium carbonate used in the reaction
increased the reaction rate significantly. Finally, compound
131 was condensed with isocyanate 132 in methylene chloride
to give sorafenib (XVIII) in 92% yield as a white solid.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anticoagulants: may enhance effect of coumarins.
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine (increased risk
of agranulocytosis).
Antivirals: avoid with boceprevir.
Metabolism
Sorafenib undergoes oxidative metabolism by CYP3A4 in the liver, as well as glucuronidation by UGT1A9 in the liver and kidneys. At steady-state, sorafenib accounts for 70-85% of the circulating analytes in plasma. About eight metabolites of sorafenib have been identified, of which five were detected in plasma.
Metabolism
Sorafenib is metabolised primarily in the liver and undergoes oxidative metabolism mediated by CYP3A4, as well as glucuronidation mediated by UGT1A9. 8 metabolites have been identified, during in vitro studies one has been shown to have equal activity to sorafenib. About 96% of a dose is excreted within 14 days, with 77%, mostly as unchanged drug, recovered in the faeces, and 19% in the urine as glucuronidated metabolites.
Storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of Sorafenib
| Melting point: | 202-204°C |
| Boiling point: | 523.3±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.454±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | White to off-white solid. |
| pka | 12.89±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 100μg/L at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 284461-73-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Sorafenib
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sorafenib
Sorafenib manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
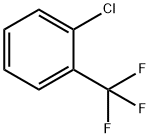
 284461-73-0 98%View Details
284461-73-0 98%View Details
284461-73-0 -
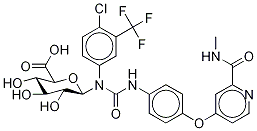
 Sorafenib 97%View Details
Sorafenib 97%View Details -
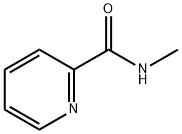
 Sorafenib 284461-73-0 99%View Details
Sorafenib 284461-73-0 99%View Details
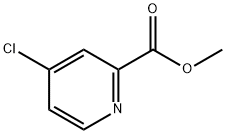
284461-73-0 -
 284461-73-0 Sorafenib 98%View Details
284461-73-0 Sorafenib 98%View Details
284461-73-0 -
 284461-73-0 98%View Details
284461-73-0 98%View Details
284461-73-0 -
 Sorafenib 98%View Details
Sorafenib 98%View Details
284461-73-0 -
 284461-73-0 Sorafenib 98%View Details
284461-73-0 Sorafenib 98%View Details
284461-73-0 -
 Sorafenib 98% (HPLC) CAS 284461-73-0View Details
Sorafenib 98% (HPLC) CAS 284461-73-0View Details
284461-73-0
