SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE
Synonym(s):4-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium salt solution
- CAS NO.:502-85-2
- Empirical Formula: C4H9NaO3
- Molecular Weight: 128.1
- MDL number: MFCD00004402
- EINECS: 207-953-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-20 16:56:23
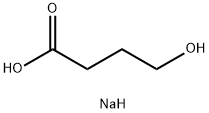
What is SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE?
Absorption
Following oral administration of sodium oxybate, GHB is released and rapidly absorbed with an absolute bioavailability of about 88%. The plasma levels of GHB increases more than dose-proportionally, with blood levels increasing 3.7‐fold as total daily dose is doubled from 4.5 g to 9 g. After administration of a single oral dose of 2.25g to 4.5g sodium oxybate, the Cmax was 27–90 μg/mL and the mean Tmax ranged from 25 to 75 minutes.
A high-fat meal delays absorption (average Tmax increased from 0.75 hr to 2 hr), reduces Cmax of GHB by 59%, and decreases systemic exposure (AUC) by 37%.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is 9690 mg/kg.
There are several cases of GHB overdose in literature where individuals ingested GHB illicitly in conjunction with other drugs and alcohol. These individuals exhibited varying degrees of depressed consciousness that may fluctuate rapidly between a confusional, agitated, combative state with ataxia and coma. Emesis (even when obtunded), diaphoresis, headache, and impaired psychomotor skills have been observed. No typical pupillary changes have been described to assist in diagnosis; pupillary reactivity to light is maintained. Blurred vision has been reported. An increasing depth of coma and acidosis have been observed at higher doses. Myoclonus and tonic-clonic seizures have been reported. Respiration may be unaffected or compromised in rate and depth. Cheyne-Stokes respiration and apnea have been observed. Bradycardia and hypothermia may accompany unconsciousness, as well as muscular hypotonia, but tendon reflexes remain intact.
In clinical trials, two adults experienced sodium oxybate overdose. One patient received an estimated dose of 150 g, which was more than 15 times the maximum recommended dose: this patient became unresponsive with brief periods of apnea and incontinent of urine and feces. The patient recovered without sequelae. The other patient died following a multiple drug overdose consisting of sodium oxybate and numerous other drugs.
There is no known antidote for sodium oxybate; therefore, overdose should be managed with general symptomatic and supportive care, with a consideration of gastric decontamination if co-ingestants are suspected.
Description
Xyrem is distributed by Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Palo Alto, CA). It is an oral solution of sodium oxybate prescribed for narcoleptic patients to treat extreme daytime sleepiness and cataplexy. Xyrem is also known as sodium oxybate which is the same as gamma hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), a drug of abuse. GHB is endogenously produced and present in the central nervous system (CNS) in small concentrations. Accidental overdosing has led to many hospitalizations and deaths. Because of the tendency to abuse GHB, it was classified as a schedule I controlled substance. This meant that GHB had a high potential for abuse and no medical purpose. However, in 2002, because of a series of clinical trials that demonstrated that the compound reduces cataplexy attacks, it was approved for use under the trademark Xyrem. Since GHB had previously been used as a ‘date-rape’ drug, Xyrem is considered a schedule III controlled substance and is distributed in accordance with strict FDA regulations. Xyrem may only be ordered through the ‘Xyrem Success Program.’ Illegal use is punishable under federal and state laws.
Description
GHB (sodium salt) (exempt preparation) (Item No. 15661) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a CNS depressant. GHB is a metabolite of γ-butyrolactone . It has a high potential for abuse. GHB is regulated as a Schedule I compound in the United States. GHB (sodium salt) (exempt preparation) (Item No. 15661) is provided as a DEA exempt preparation. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder
The Uses of SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE
4-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium salt is an agonist to both GHB and GABAB neural receptors, exhibiting neurotransmitter-like effects. It has been used as a general anesthetic in treatment for sleep disorders and clinical depression, but also has been identified as a “date rape drug”.
The Uses of SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE
antibacterial
The Uses of SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE
Xyrem is used as a prescription drug for the treatment of cataplexy in patients with narcolepsy. It can also be used illegally for recreational purposes as well as drug-facilitated sexual assault.
Background
Sodium oxybate (Xyrem) is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant used to treat cataplexy or excessive daytime sleepiness associated with narcolepsy. It is a sodium salt of gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid, an endogenous cerebral inhibitory neurotransmitter and a metabolite of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. Due to its physiological effects, sodium oxybate is associated with a risk for substance misuse and abuse. Sodium oxybate has been misused to stimulate body growth and to induce euphoria, disinhibition, and sexual arousal as a "party drug" or "club drug." For safety reasons, sodium oxybate is a controlled substance only available through a restricted program in approved countries.
An extended-release oral suspension formulation of sodium oxybate for narcolepsy, marketed under the brand name LUMRYZ, gained tentative FDA approval in July 2022 and was fully approved in May 2023. In some countries, sodium oxybate has been investigated and used in alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) to aid abstinence maintenance in alcohol use disorders.
Indications
Sodium oxybate is a central nervous system depressant indicated for the treatment of cataplexy or excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) in patients with narcolepsy. In the US and in Europe, the drug is approved for use in patients 7 years of age and older while in Canada, it is not recommended in children under the age of 18, unless clearly needed.
Indications
The substance is related to γ-aminobutyric acid, a cerebral metabolite that is supposed to be sleep inducing. When given i.p., it produces a shallow anesthesia (tolerance stage a: paralysis of the spinal cord and mesencephalon, slight relaxation of the muscles) that resembles natural sleep as seen via the electroencephalograph. It is employed as an anesthetic during labor and in combination anesthesia with nitrous oxide, barbiturates, or neuroleptanalgesics.
brand name
Xyrem (Jazz).
Pharmacokinetics
Sodium oxybate works to improve nocturnal sleep, improve alertness the following day, and ameliorate cataplexy. Decreased excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy is observed in higher doses and at a delayed time. It is proposed that sodium oxybate increases the time spent in Stages N2 and N3 of sleep and decreases the shift to stages N1/Wake/REM, resulting in improved continuity of sleep and deeper sleep.
Sodium oxybate is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant that can cause significant respiratory depression. Due to its physiological and psychological effects, sodium oxybate is associated with a risk for substance misuse and abuse, addiction, withdrawal syndrome, and overdoses. Sodium oxybate is a sodium salt of GHB, a naturally occurring CNS depressant that increases dopamine levels and increases serotonin turnover. Sodium oxybate stimulates growth hormone release, often leading to its misuse as a dietary supplement for bodybuilding. In patients with narcolepsy, sodium oxybate increases nocturnal growth hormone secretion and slow-wave sleep at night, which is when growth hormone is typically released.
Environmental Fate
Xyrem is a water-soluble white to off-white powder, which can be disposed by dumping the oral solution down the sanitary sewer system. This is the preferred method of disposal for drugs which have a high potential for abuse and/or accidental overdose.
Metabolism
Animal studies suggest that metabolism is the major elimination pathway for GHB, producing carbon dioxide and water via the tricarboxylic acid (Krebs) cycle and secondarily by beta-oxidation. GHB dehydrogenase, a cytosolic NADP+-linked enzyme, converts GHB to succinic semialdehyde, which is then biotransformed to succinic acid by succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase. Succinic acid enters the Krebs cycle where it is metabolized to carbon dioxide and water. A second mitochondrial oxidoreductase enzyme, a transhydrogenase, also catalyzes the conversion to succinic semialdehyde in the presence of α-ketoglutarate. GHB can alternatively be converted to carbon dioxide and water via β-oxidation mediated by 3,4-dihydroxybutyrate. No active metabolites have been identified.
Toxicity evaluation
GHB is endogenously present in the brain and at low concentrations binds to GHB receptors that are excitatory. This effect can cause euphoria, making it a drug of abuse at ‘rave’ parties. However, at higher concentrations, Xyrem is a CNS depressant and this is the main mechanism of its toxicity. The negative effects are mediated by the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)B receptors. The maximum stimulation of these receptors by GHB is w69% when compared to the binding of a GABAB receptor agonist. Therefore, the drug appears to be a weak agonist of the GABA-binding site of GABAB receptors. Overdose can lead to respiratory arrest and death. The combined use of other sedative hypnotic agents or alcohol can exacerbate the toxicity of Xyrem.
Properties of SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE
| Melting point: | 145-146°C |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | Controlled Substance, -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | solid |
| Merck | 13,4840 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 502-85-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Butanoic acid, 4-hydroxy-, monosodium salt (502-85-2) |
Safety information for SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for SODIUM 4-HYDROXYBUTYRATE
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 502-85-2 Sodium oxybate 99%View Details
502-85-2 Sodium oxybate 99%View Details
502-85-2 -
 502-85-2 99%View Details
502-85-2 99%View Details
502-85-2 -
 GHB sodium salt solution CAS 502-85-2View Details
GHB sodium salt solution CAS 502-85-2View Details
502-85-2 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
