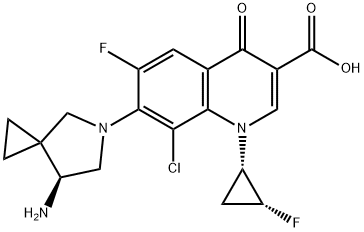
Sitafloxacin Sesquihydrate
Synonym(s):7-[(7S)-7-Amino-5-azaspiro[2.4]hept-5-yl]-8-chloro-6-fluoro-1-[(1R,2S)-2-fluorocyclopropyl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid, hydrate (2:3);
- CAS NO.:163253-35-8
- Empirical Formula: C19H20ClF2N3O4
- Molecular Weight: 427.83
- EINECS: 1308068-626-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
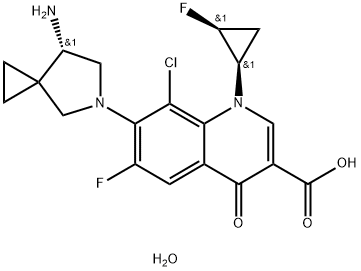
What is Sitafloxacin Sesquihydrate?
Description
The fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent sitafloxacin hydrate was developed by Daiichi Sankyo and was approved and launched last year in Japan. Sitafloxacin’s mode of action is through inhibition of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. It is indicated for the treatment of inflammatory infections such as laryngopharyngitis, adenoiditis, acute bronchitis, pneumonia, secondary infections due to chronic respiratory lesions, cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, cervicitis, otitismedia, sinusitis, periodontitis, and pericoronitis and jaw inflammation. Due to its broad spectrum of potent antibacterial activity, sitafloxacin is expected to be clinically effective in treating severe cases of bacterial infection, relapse/recrudescence of infection and infections in which resistant bacteria are suspected to be the cause.
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
The Uses of Sitafloxacin Sesquihydrate
Sitafloxacin is a new-generation, broad-spectrum oral fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It is very active against many Gram-positive, Gram-negative and anaerobic clinical isolates, including strains resistant to other fluoroquinolones, was recently approved in
The Uses of Sitafloxacin Sesquihydrate
Antibacterial
Side Effects
The most commonly reported adverse reactions include rash, dizziness, headache, diarrhea, loose stool, stomach discomfort, abdominal bloating, abdominal pain, constipation, indigestion, nausea and stomatitis.
Synthesis
The optically pure fluorocyclopropylamine 111 intermediate was prepared as described in thescheme. Condensation of diphenylmethyl amine 104 with acetaldehyde followed by treatment with trichloromethyl chloroformate in the presence of triethylamine gave N-vinyl carbamoyl chloride 105 in 53% yield. This intermediate was reacted with sodium benzyloxide (generated in situ) to afford N-vinylcarbamate 106 in 82% yield. Fluorocyclopropanation of 106 with zinc¨C monofluorocarbenoid generated from fluorodiiodomethane and diethylzinc provided N-(2-fluorocyclopropyl)carbamate 107 in 90% yield and with a diastereomeric ratio of 93:7 favoring the cis-isomer. Hydrogenolysis of the CBz and the diphenylmethyl groups was accomplished with catalytic 10% palladium on charcoal and was followed by treatment with TsOH to afford dl-108 as its tosylate salt. Acylation of dl- 108 TsOH with l-menthyl chloroformate gave a 1:1 mixture of the diastereomeric carbamate 109 which upon four repeated recrystallizations from hexane/ethyl acetate afforded optically pure 110 in 26% yield. Acidic hydrolysis of 110 furnished 111 as its HCl salt in 88% yield.

Mode of action
Sitafloxacin inhibits DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are involved in bacteria DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination. Sitafloxacin has less activity against human topoisomerase II, an enzyme involved in cell growth. According to Akasaka et al. DNA gyrase, consisting of the subunits GyrA and GyrB, has ATP-dependent DNA supercoil-ing activity and is a primary target of quinolones in Gram-negative species, such as Escherichia coli and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. In contrast, topoisomerase IV, consisting of the subunits ParC and ParE, has an essential role in partitioning replicated chromosomes and is more sensitive than DNA gyrase to some quinolones, such as levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in the Gram-positive species, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae[1].
References
[1] Ghebremedhin, B. “Bacterial Infections in the Elderly Patient: Focus on Sitafloxacin.” 2012. 0.
Properties of Sitafloxacin Sesquihydrate
| Melting point: | 145-147°C (dec.) |
| alpha | 589 -199.9° |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Aqueous Base (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Very Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 163253-35-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Sitafloxacin Sesquihydrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sitafloxacin Sesquihydrate
| InChIKey | ANCJYRJLOUSQBW-UWQPBFEBNA-N |
| SMILES | N[C@@H]1CN(C2=C(C=C3C(=O)C(C(=O)O)=CN([C@@H]4C[C@@H]4F)C3=C2Cl)F)CC21CC2.O |&1:1,16,18,r| |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![Carbamic acid, [(7S)-5-(phenylmethyl)-5-azaspiro[2.4]hept-7-yl]-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS2/GIF/144282-37-1.gif)



You may like
-
 Sitafloxacin sesquihydrate CAS 163253-35-8View Details
Sitafloxacin sesquihydrate CAS 163253-35-8View Details
163253-35-8 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
