Silymarin
- CAS NO.:65666-07-1
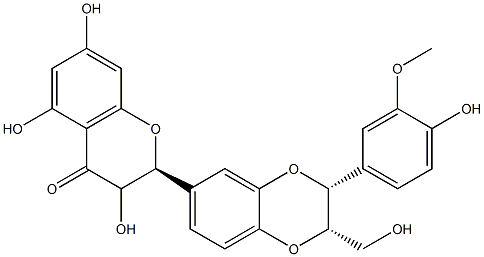
- Empirical Formula: C25H22O10
- Molecular Weight: 482.44
- MDL number: MFCD01776359
- EINECS: 613-830-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-10 11:33:04

What is Silymarin?
The Uses of Silymarin
Silymarin a flavonolignan complex extracted from milk thistle, has been shown to provide cytoprotective, antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects. Provides extracts such as (+)-taxifolin as an inhibitor of β-amyloid aggregation.
The Uses of Silymarin
Silymarin has been used to study:
- its in vitro antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal activities and cytotoxicity
- its effect of silymarin on bladder contractions in cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis rat model
- its effect on liver toxication induced by Fumonisin B1 in mice
Indications
Milk thistle (Silybum [Carduus] marianus) is a spiny European plant with white-veined leaves and milky sap, the seed of which is used to treat liver disease.Milk thistle seed extract is used orally in the treatment of alcoholic and other cirrhoses and in Europe intravenously for its hepatoprotective effect in Amanita and other mushroom poisonings. It is grown in this country primarily as a “liver cleanser” and is reputed to protect this organ from a wide array of toxins.Milk thistle seed contains the active principle silymarin, a complex of flavonolignan compounds including silibinin (silybin), silidianin, and silychristin.
Definition
ChEBI: 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-[3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-4-one is a flavonolignan.
General Description
Silymarin is a flavonolignan, obtained from milk thistle (Silybum marianum) plant.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Silymarin was shown to protect the liver from the cytotoxic effects of anti-tuberculosis drugs by decreasing serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels. This effect was related to the anti-oxidant effects of silymarin.
Mechanism of action
Silymarin is thought to protect the liver by preventing the entry of toxins into the hepatocyte and by stimulating nucleolar polymerase A, which, in turn, increases protein synthesis and liver regeneration. Silymarin undergoes enterohepatic circulation, increasing its concentration in hepatocytes. It is also an antioxidant in its own right and is considered to have some cytoprotective effect against carcinogens.
Mechanism of action
Silybum marianum (milk thistle) contains numerous phytocompounds, such as silymarin and silibinin, demonstrating antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. Silibinin has strong protection against UV-induced damage by inhibition in both cell proliferation and apoptosis by reducing thymine dimer-positive cells and upregulating p53 in mice. Increasing the transcriptional activity of p53 leads to the synthesis of p21/Cip1, a protein that arrests DNA synthesis and thereby increases DNA repair time.
Clinical Use
Alcoholic cirrhosis has been improved (faster return
of liver enzymes to baseline) in at least three trials, although
one multicenter Spanish study failed to
demonstrate any change in the clinical course.There is
no evidence to support the use of milk thistle to increase
alcohol tolerance, although it is certainly being
used for this purpose. The effectiveness of silymarin
for viral hepatitis is not clear, although several trials
demonstrated enough benefit to encourage further
studies.
Intravenous silymarin has been demonstrated to
lower mortality from Amanita mushroom poisonings,
but this formulation is available only in Europe.Animal
studies have demonstrated hepatic protection against
alcohol, acetaminophen, and mushroom toxins and protection
against hepatic fibrosis with bile duct occlusion.
There is also evidence of silybin protecting against cisplatin-
induced nephrotoxicity in rats. It is not yet clear
whether milk thistle extract offers any renal protection
to humans.
Side Effects
Milk thistle appears to be remarkably safe, with loose stools due to increased bile solubility and occasional allergic reactions being the common side effects. It has not been evaluated in children or in pregnant women.There are no known serious drug or herb interactions.
Toxicity evaluation
Silymarin has been known for its very low toxicity, Acute toxicity studies of silymarin after intravenous infusion have been carried out in mice, rats, rabbits and dogs. The LD50 values were 400 mg/kg in mice, 385 mg/ kg in rats, and 140 mg/kg in rabbits and dogs though these values were dependent on infusion rate. With slow infusion rate (over 2 to 3 h) the LD50 increased to 2 g/kg in rats and after oral administration it was even 10 g/kg.
Properties of Silymarin
| Melting point: | 158 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Acetone (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Very Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Light Orange to Brown |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C25H22O10/c1-32-17-6-11(2-4-14(17)28)24-20(10-26)33-18-7-12(3-5-16(18)34-24)25-23(31)22(30)21-15(29)8-13(27)9-19(21)35-25/h2-9,20,23-29,31H,10H2,1H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 65666-07-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Silymarin
Computed Descriptors for Silymarin
| InChIKey | FDQAOULAVFHKBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(C2=CC=C3OC(C4=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C4)C(CO)OC3=C2)OC2=CC(O)=CC(O)=C2C(=O)C1O |
Silymarin manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 3-Nitrobenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran







You may like
-
 65666-07-1 Silymarin 98%View Details
65666-07-1 Silymarin 98%View Details
65666-07-1 -
 Silymarin CAS 65666-07-1View Details
Silymarin CAS 65666-07-1View Details
65666-07-1 -
 Silymarin CAS 65666-07-1View Details
Silymarin CAS 65666-07-1View Details
65666-07-1 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0